CAA News Today
SCOTUS Ruling on Affirmative Action: CAA ED Response
posted by CAA — June 30, 2023
The US Supreme Court ruling invalidating race-conscious admissions considerations at colleges and universities is antithetical to CAA’s mission, specifically our commitment to the diversity of practices and practitioners in the visual arts and academia. This is another in a series of blows to the field, the reverberations of which will be felt for generations to come.
Justice Clarence Thomas dismissing affirmative action policies at universities as “rudderless, raced-based preferences” demonstrates a deliberate suppression of the entire history of institutional racism in this country, which by design actively obstructs opportunity and access for so many.
Now more than ever, we must come together as an organization and develop alternative strategies for ensuring equity and representation in a meaningful way, without performativity or tokenism. Even with affirmative action policies in place, many important voices were relegated to the margins; this ruling will only serve to repress them further. We have a responsibility to continue fighting to center and amplify such voices.
Despite this current era of national regression in the realm of human rights, I still have faith we can have an impact, learn from a problematic past, and reshape the future of the field. Join me in continuing to transform pain into purpose.
Meme Omogbai
Executive Director & CEO
CAA | Advancing Art and Design
CAA 2021: A look back on the past year’s programming, publications, and opportunities
posted by CAA — November 30, 2021
CAA has produced this reel with a compilation of events, scholarship, programs, and initiatives CAA from the last year. See below for a full list of each item (in order of appearance in the video) with links to learn more.
Programming:
CAA’s first virtual Annual Conference
Mariam Ghani in conversation with Laura Anderson Barbata
In Conversation with Dr. Nancy Odegaard
Theresa Avila, Annual Conference Program Chair in conversation with Meme Omogbai
An Inaugural Evening with CAA Distinguished Awardees and Artists
CAA Then & Now: Reflections on the Centennial Book and the Next Century
Karen Leader, author of Chapter 12: Advocacy
Opportunities:
Publication, travel, and support grants
Publications and Publications Programming:
Artist Project, Elana Mann for Art Journal Open
Roundtable discussion for Art Journal Open, Holding Space…
Art Journal and The Art Bulletin
caa.reviews book and exhibition reviews
caa.reviews’s dissertation roster, 2020
Global Programs
CAA-Getty International Program
CAA-Getty 10-Year International Program online publication
Podcasts
CAA Conversations by CAA’s Education Committee
CAA’s 110th Annual Conference will take place in Chicago from February 17-19, followed by virtual live sessions to be held in Zoom from March 3-5. For more information and to register go to this link.
CAA Solidarity Statement
posted by CAA — June 05, 2020

The College Art Association (CAA) condemns all forms of systemic racism, violence, bias, aggression and the marginalization of Black, Indigenous, and all Peoples of Color (BIPOC) as well as discrimination based on race, intersectionality, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. As a community of those who study, teach, write about, advocate for and/or create art and design, we have committed our life’s work to learning-from, exploring-with, and creating-towards our shared humanity. As a membership organization we choose to use our voices to speak to one another and speak up for one another.
To ensure lasting change:
- We encourage the creative community to examine biases, micro-aggressions, and who we leave out.
- We encourage learning from sharing narratives of BIPOC.
- We encourage providing services and support for underrepresented and entirely non-represented members of the community.
- We will work to create and promote standards and systems that actively support equity in anti-racist teaching, research, publication and creative practices.
In solidarity, CAA, its board, and its staff continue to amplify equity, diversity, and inclusion and call our community to action with us in this commitment to change.
CAA Values Statement on Diversity and Inclusion
For additional resources see the Committee on Diversity Practices as well as resources shared via CAA News, Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook.
Announcing the 2020 Recipients of the Art History Fund for Travel to Special Exhibitions
posted by CAA — May 12, 2020

Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam
In fall 2018, we announced CAA had received an anonymous gift of $1 million to fund travel for art history faculty and their students to special exhibitions related to their classwork. The generous gift established the Art History Fund for Travel to Special Exhibitions.
The jury for the Art History Fund for Travel to Special Exhibitions has now selected the second group of recipients as part of the gift. This year’s awardees are:
Holly Flora, Tulane University, New Orleans, LA
Course: Art, Cosmopolitanism, and Intellectual Culture in the Middle Ages
Exhibition: Medieval Bologna: Art for a University City at the Frist Center for the Visual Arts, Nashville, TN
Caroline Fowler, Clark Art Institute, Williamstown, MA
Course: Slavery and the Dutch Golden Age
Exhibition: Slavery at the Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam
Maile Hutterer, University of Oregon, Eugene, OR
Course: Time in Medieval Art and Architecture
Exhibition: Transcending Time: The Medieval Book of Hours at The Getty Center, Los Angeles, CA
Erin McCutcheon, Lycoming College, Williamsport, PA
Course: Art & Politics in Latin America
Exhibition: Rafael Lozano-Hemmer: Unstable Presence at SFMOMA, San Francisco, CA
Shalon Parker, Gonzaga University, Spokane, WA
Course: Women Artists
Exhibition: New Time: Art and Feminisms in the 21st Century at the Berkeley Art Museum and Pacific Film Archive, Berkeley, CA
Rebecca Pelchar, SUNY Adirondack, Queensbury, NY
Course: Introduction to Museum Studies
Exhibition: Marcel Duchamp: The Barbara and Aaron Levine Collection at the Hirshhorn Museum, Washington, DC
As museums and schools have moved online in light of the coronavirus pandemic, we are being as flexible as necessary with the dates of travel to accommodate all award winners and classes.
The Art History Fund for Travel to Special Exhibitions supports travel, lodging, and research efforts by art history students and faculty in conjunction with special museum exhibitions in the United States and throughout the world. Awards are made exclusively to support travel to exhibitions that directly correspond to the class content, and exhibitions on all artists, periods, and areas of art history are eligible.
Applications for the third round of grants will be accepted by CAA beginning in fall 2020. Deadlines and details can be found on the Travel Grants page.
CAA Statement on Firing of Graduate Student Strikers at UC Santa Cruz
posted by CAA — March 12, 2020

UCSC graduate students on strike, March 2020. Photo: Mat Weir, via GoodTimes
The CAA Advocacy Committee approved the following statement in March 2020.
CAA condemns the termination of employment for graduate student strikers at the University of California, Santa Cruz, calls for their reinstatement, and urges the university to commence negotiations with the students as soon as possible. This action has affected graduate students in the visual arts, which will impact their lives in serious ways, including the loss of medical insurance and residency status. We consider that their demands for an appropriate augmentation of salary in line with the increased costs of living are legitimate and note that they now have the support of the UAW, with whom the university is contracted.
Graduate students are indispensable workers who cannot be expected to execute their teaching duties and to pursue their own research when housing and food costs are not affordable with their current wages. CAA maintains that graduate students should be compensated at a level that makes it possible for them to flourish on campus as research assistants, teachers, and emerging scholars. A fair wage correlated with cost of living increases is a necessary precondition for their own work, essential to fulfilling the educational mandate of their departments, and essential for the dignity of all workers at the university. To punish students for exercising their rights to demand a decent wage is, in our view, unjust and unacceptable, and all penalties should be reversed immediately.
Further Reading
UC Graduate Students Threaten More Strikes as Movement Grows (Los Angeles Times)
Why We’re Striking for Fair Teaching Wages at UC Santa Cruz — Even With a Baby on the Way (Washington Post)
California University Fired 54 Grad Students Who Were Striking for Higher Pay (CNN)
Why Graduate Students at UC Santa Cruz Are Striking (New York Times)
CAA Standards and Guidelines for Part-Time Professional Employment (CAA)
CAA Invites Proposals Related to Climate Crisis at 2021 Annual Conference
posted by CAA — February 26, 2020

Fridays For Future protest in Toronto, Canada. Photo: Jasmin Sessler
As part of the 2021 Annual Conference, CAA seeks to offer a selection of sessions, papers, speakers, and related programming on the topic of Climate Crisis. Including but going beyond eco-art and eco-criticism, and with climate justice and intersectional thinking as priorities, panels and presentations can address ecology as a matter of the content of artworks, but also, and pressingly, how we—artists, designers, and art historians, institutional stakeholders and independent practitioners, and members of allied fields—can and should change our professional practices in light of the crisis.
We invite discussions of creative interventions into the status quo, up to and including a serious discussion of ways of reducing the carbon footprint of the annual conference itself, while preserving and enhancing access. Practices and themes may include remediation and amelioration, thematic representation and critique, the ramifications of change for institutions and collections, issues of preservation, and the nature of research. We invite radical and practical proposals. The conference content will stress a broad and inclusive conversation on climate crisis impact through the lens of age; gender; nationality; race; religion; and socioeconomic status among others.
Announcing the 2020 Awards for Distinction Recipients
posted by CAA — February 04, 2020
Honorees this year include Eleanor Antin, Joseph Leo Koerner, Maud K. Lavin, Annet Couwenberg, Harriet Senie, Kyle Staver, and many other scholars, artists, and teachers
CAA Annual Conference, Chicago, February 12-15, 2020

Eleanor Antin
We are pleased to announce the recipients and finalists of the 2020 CAA Awards for Distinction. Among the winners this year is Eleanor Antin, recipient of the 2020 Distinguished Artist Award for Lifetime Achievement. Born in the Bronx in 1935 to immigrant parents, Antin is an innovator and pioneer as a feminist artist, a performance and installation artist, a conceptual artist, filmmaker, and writer. She is an emeritus Professor of Visual Arts at the University of California, San Diego and author of several books including An Artist’s Life by Eleonora Antinova and Conversations with Stalin. Antin’s solo museum exhibitions have appeared at the MoMA, the Whitney Museum, and, in 2019, the Los Angeles County Museum of Art with her retrospective, Eleanor Antin: Time’s Arrow. Her awards include a Guggenheim Fellowship and a 2006 Women’s Caucus for Art Lifetime Achievement Award.

Joseph Leo Koerner
Joseph Leo Koerner is the recipient of the 2020 Distinguished Lifetime Achievement Award for Writing on Art. His achievements include four landmark books on sixteenth-century paintings: The Moment of Self-Portraiture in German Renaissance Art (University of Chicago Press, 1993), The Moment of Self-Portraiture in German Renaissance Art (University of Chicago Press, 2003), The Reformation of the Image (Reaktion Books, 2004), and Bosch and Bruegel: From Enemy Painting to Everyday Life (Princeton University Press, 2016). Koerner has also written widely on more recent artists, from Caspar David Friedrich to Paul Klee, and explored early-twentieth century Vienna through a documentary project and a semi-autobiographical film.

Maud K. Lavin
Dr. Maud K. Lavin is the recipient of the 2020 Distinguished Feminist Award for scholarship. Over the course of three decades, Lavin has worked tirelessly as a key pioneer in the field of feminist art history and visual studies. She is the author of numerous books including the first English-language book on Berlin Dada artist Hannah Hoch, Cut with the Kitchen Knife: The Weimar Photomontages of Hannah Hoch (Yale University Press, 1993), and most recently, Boys’ Love, Cosplay, and Androgynous Idols: Queer Fan Cultures in Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan, co-edited with Ling Yang and Jamie Zhao (Hong Kong University Press, 2017). She is a professor of Visual and Critical Studies and Art History, Theory, and Criticism at the School of the Art Institute of Chicago.
The Awards for Distinction will be presented during Convocation at the CAA Annual Conference on Wednesday, February 12 at 6:00 PM at the Hilton Chicago. This event is free and open to the public.
The full list of 2020 CAA Awards for Distinction Recipients
Distinguished Artist Award for Lifetime Achievement
Eleanor Antin
Distinguished Lifetime Achievement Award for Writing on Art
Joseph Leo Koerner
Distinguished Feminist Award—Scholar
Maud K. Lavin
Distinguished Teaching of Art Award
Annet Couwenberg
Distinguished Teaching of Art History Award
Harriet Senie
Artist Award for Distinguished Body of Work
Kyle Staver
CAA/AIC Award for Distinction in Scholarship and Conservation
Jeanne Marie Teutonico
Award for Excellence in Diversity
3Arts
Outstanding Leadership in Philanthropy Award
Terra Foundation for American Art
Charles Rufus Morey Book Award
J. P. Park
A New Middle Kingdom: Painting and Cultural Politics in Late Chosŏn Korea (1700–1850)
University of Washington Press, 2018
Finalists
Chanchal B. Dadlani
From Stone to Paper: Architecture as History in the Late Mughul Empire
Yale University Press, 2019
Barbara Furlotti
Antiquities in Motion: From Excavation Sites to Renaissance Collections
Getty Publications, 2019
Matthew Looper
The Beast Between: Deer in Maya Art and Culture
University of Texas Press, 2019
Alfred H. Barr Jr. Award
Karl Kusserow and Alan C. Braddock
Nature’s Nation: American Art and Environment
Princeton University Art Museum, 2019
with contributions by Miranda Belarde-Lewis, Teddy Cruz, Rachael Z. DeLue, Mark Dion, Fonna Forman, Laura Turner Igoe, Robin Kelsey, Anne McClintock, Timothy Morton, Rob Nixon, Jeffrey Richmond-Moll, Kimia Shahi, and Jaune Quick-to-See-Smith
Honorable Mention
Esther Gabara
Pop América, 1965–1975
Duke University Press, 2018
Finalists
Cathleen Chaffee
Introducing Tony Conrad: A Retrospective
Albright-Knox Art Gallery, Buffalo, NY, in association with Koenig Books, London, 2019
Jessica Morgan and Alexis Lowry
Charlotte Posenenske: Work in Progress
Dia Art Foundation and Walther König, 2019
Elizabeth Morrison
Book of Beasts: The Bestiary in the Medieval World
Getty Publications, 2019
Alfred H. Barr Jr. Award for Smaller Museums, Libraries, Collections, and Exhibitions
Denise Murrell
Posing Modernity: The Black Model from Manet and Matisse to Today
Yale University Press in association with The Miriam and Ira D. Wallach Art Gallery, Columbia
University in the City of New York, 2018
Honorable Mention
Phillip Earenfight
Shan Goshorn: Resisting the Mission
Trout Gallery, Dickinson College, 2019
Finalists
Tracy L. Adler
Jeffery Gibson: This is The Day
Prestel Publishing, 2018
Faith Brower, Heather Ahtone, and Seth Hopkins
Warhol and the West
University of California Press, 2019
Frank Jewett Mather Award for Art Criticism
Darby English
To Describe a Life: Notes from the Intersection of Art and Race Terror
Yale University Press, 2019
Art Journal Award
Philip Glahn and Cary Levine
“The Future Is Present: Electronic Café and the Politics of Technological Fantasy”
Art Journal, vol. 78, no. 3 (Fall 2019): 100–121
Arthur Kingsley Porter Prize
Claudia Brittenham
“Architecture, Vision, and Ritual: Seeing Maya Lintels at Yaxchilan Structure 23″
The Art Bulletin, vol. 101, no. 3 (September 2019): 8–36
Learn about the juries that select the recipients of the CAA Awards for Distinction.
Submit a Proposal for Idea Exchange at CAA 2020
posted by CAA — September 16, 2019
We launched Idea Exchange at the 2018 Annual Conference in Los Angeles in response to members who expressed an interest in holding informal roundtable discussions on topics ranging from fellowship applications and gallery representation to student engagement in the classroom and preserving women artists’ legacies. See a list of previous discussion topics here.
We’re offering Idea Exchange again in 2020 and we’re looking for CAA members to serve as discussion leaders.
Propose a topic that you would like to discuss with your colleagues for a sixty-minute roundtable at the conference. It can relate to professional development, teaching, or current events, such as the debate surrounding Confederate monuments or the #MeToo movement in the arts. Be creative. The conversations are meant to be lively and engaging. Please submit your Idea Exchange proposals by November 1, 2019.
In order to submit an Idea Exchange topic, you will need to have your member ID and password ready. If you do not have an individual ID number and password or you do not know it, please contact member services by email at membership@collegeart.org or by phone at 212-691-1051, ext. 1.
Idea Exchange will be held in the Hilton Chicago, Lower Level, Salon B, during the following times:
Wednesday, February 12: 10:30 AM; 12:30 PM; 2:00 PM; 4:00 PM
Thursday, February 13: 10:30 AM; 12:30 PM; 2:00 PM; 4:00 PM
Friday, February 14: 10:30 AM; 12:30 PM; 2:00 PM; 4:00 PM
Saturday, February 15: 10:30 AM; 12:30 PM
For more information on Idea Exchange, contact Mira Friedlaender, manager of the Annual Conference, at mfriedlaender@collegeart.org or by phone at (212) 392-4405.
An Interview with Amy Meyers, Recently Retired Director of the Yale Center for British Art
posted by CAA — July 26, 2019
In June, Amy Meyers ended a long and fruitful career as Director of the Yale Center for British Art, which she led for seventeen years. Prior to her appointment in 2002, she spent much of her career at research institutes including Dumbarton Oaks; the Center for Advanced Study in Visual Arts at the National Gallery of Art, Washington, DC; and The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens. She also taught at the California Institute of Technology, the University of Michigan, Mount Vernon College, and Yale, and has written extensively on the visual and material culture of natural history in the transatlantic world.
Joelle Te Paske, CAA Media and Content Manager, corresponded with Amy over email to reflect upon her tenure at the YCBA, her experiences with CAA, and her plans for the future. Read the interview below.
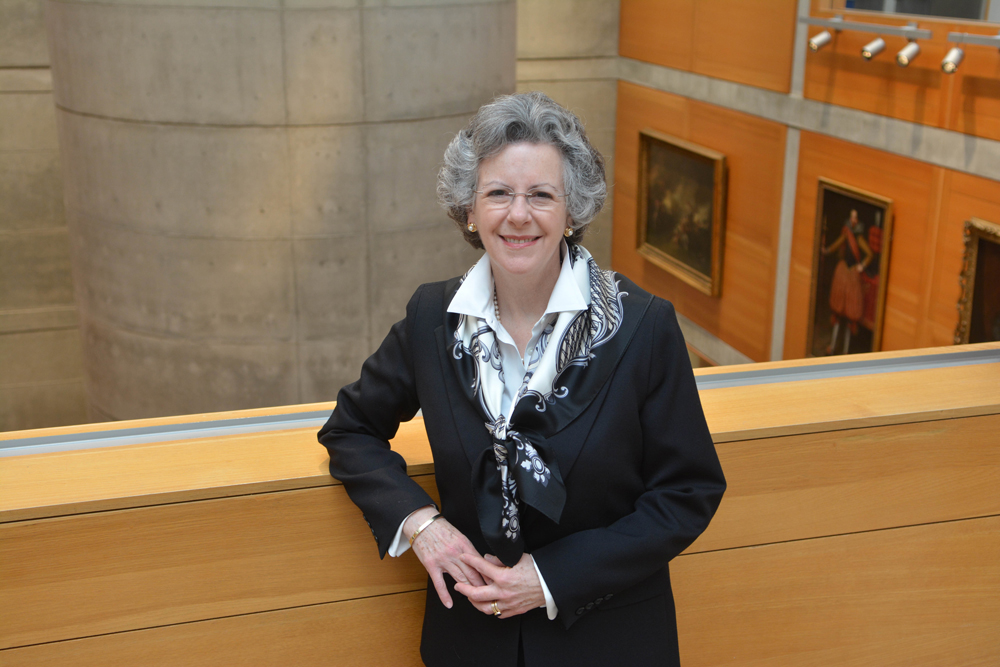

Amy Meyers, Yale Center for British Art, photo by Michael Marsland
Joelle Te Paske: Amy, thank you so much for speaking with us. To begin, what pathways led you to the Yale Center for British Art (YCBA)?
Amy Meyers: There is no question that my experiences as a graduate student at Yale set the stage for my return to direct the Yale Center for British Art 25 years following my arrival as a doctoral candidate in American Studies, in the fall of 1977—the first year the magnificent collections of the newly opened YCBA were accessible to students.

Long Gallery after reinstallation, Yale Center for British Art, photo by Richard Caspole
I had come to Yale to write a dissertation on the photographers who accompanied the federal geological surveys of the American West following the Civil War, and my interest in the art of empire brought me to explore the staggering collections of paintings, prints, drawings, maps, rare books, and manuscripts amassed by the Center’s founder, Paul Mellon, relating to the depiction of the natural world, particularly in the Americas.

John Ruskin, Study of an Oak Leaf, undated, pen and brown ink with watercolor over graphite heightened with gouache and gum; verso: graphite on paper, Yale Center for British Art, Paul Mellon Collection
The following spring, I enrolled in one of the first courses held at the Center—a seminar on Ruskin, taught by George Hersey. That course included students not only from the Department of the History of Art, but others, who, like me, were interested in the influence of Ruskin’s thought on many aspects of culture, particularly science. Professor Hersey’s important consideration of Ruskin as a major thinker of the nineteenth century, and the discussions that took place in that class between and amongst students, were foundational to my graduate education. I formed collegial friendships with many students who would go on to contribute significantly to art historical scholarship, both in academe and in museums, including David Curry, Bruce Robertson, George Shackelford, Mark Simpson, and Scott Wilcox—and these friendships have informed my scholarship and influenced the way in which I have approached the programs I have had the privilege to run, from the Virginia Steele Scott Gallery of American Art at the Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens, to the YCBA.
The interdisciplinarity of Professor Hersey’s class reflected Yale’s commitment to exploration across disciplinary boundaries in many areas of study—a commitment that was unusual at American universities in the 1970s. Jules Prown, who had been the YCBA’s first director, creating the institution in concert with Paul Mellon and a distinguished committee of Yale faculty members, was himself devoted to examining the history of art from a broad range of vantage points, and he and his colleagues built that approach into the Center’s culture, both as a research institute and as a public museum with teaching at its heart.

Unidentified man, Paul Mellon, Kenneth Froeberg, and Jules Prown, during the construction of the Yale Center for British Art, 1974, photo by William B. Carter, Yale Department of Public Information, Institutional Archives, Yale Center for British Art
I was privileged not only to study with Jules, but to have him as one of my dissertation advisors. I learned from him the value of the close examination of objects as primary to art historical research, as well as the importance of working collaboratively with groups of scholars in developing the richest, most productive, and enjoyable of research communities. Jules drew around him, through his exciting classes and seminars, a large and devoted coterie of students from across the university who were interested in cross-cultural studies, including art history and material culture—a field he was instrumental in driving forward. Many of the students who took George Hersey’s seminar were part of this group; but others, including Margaretta Lovell (who by then was teaching a course on material culture with Jules), David Lubin, Angela Miller, Rodger Birt, Esther Thyssen, Buffy Easton, Valerie Steele, Catherine Lynn, Rebecca Zurier, Kenneth Haltman, Alexander Nemerov, Richard Powell, and Helen Cooper (who already was serving as Curator of American Paintings at the Yale University Art Gallery) also were active members of Jules’s circle of students (and there were many others who were off writing dissertations, such as Kathleen Foster, or who had graduated relatively recently and were known to us by their groundbreaking work, such as David Solkin). At that time, Bryan Wolf was a young professor of English literature and American Studies who had developed a strong interest in American art, and he also was an important member of Jules’s circle. I was tremendously privileged to have Bryan as one of my dissertation advisors, as well.
The sadly short-lived Center for the Study of American Art and Material Culture, directed by Richard Beard, was established by Robert McNeil, through the Barra Foundation, at the Yale University Art Gallery in the same year that the YCBA opened.

A Survey of American Photographs 1840–1940, installation as presented from March 28–June 6, 1978, organized by the Yale Center for American Art and Material Culture, photo courtesy of the Yale University Art Gallery Institutional Archives
This center both reinforced the community of Americanists at Yale and gave me the opportunity to curate the first of my own exhibitions, American Photographs: 1840 to 1940. The group of Western American historians fostered by my third dissertation advisor, Howard Lamar, and Archibald Hanna, the then-curator of Western Americana at the Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library, also promoted a culture of intellectual exchange, focused quite centrally on the visual culture of the West. Additionally, the American Studies Program offered students and faculty members with cross-disciplinary interests a supportive environment that encouraged innovative, experimental approaches to the study of American culture across the board. Collectively, these centers and programs taught graduate students of my generation at Yale the value of being a member of an engaging and supportive community of intellectual interchange, supported institutionally, and I have no doubt that this experience influenced my interest in being involved in study centers over the course of my professional career.
Indeed, as a graduate student, I was introduced to the vibrant culture of international research institutes when I was awarded a junior fellowship at Harvard University’s Washington-based research institute, Dumbarton Oaks (DO), my dissertation topic having shifted to a broader consideration of the relation of the visual arts to the natural sciences, from the colonial period, through the establishment of the republic, and into the nineteenth century. Some of my closest collegial friendships were formed in the community of DO, including my life-long professional partnership with Therese O’Malley, with whom I presently am organizing an exhibition on John and William Bartram and the emergence of environmental thought in America.

Therese O’Malley and Amy Meyers at a conference at the Royal Botanic Gardens at Kew, 2005.
Therese and I were privileged to be hired by the first dean of the Center for Advanced Study in the Visual Arts (CASVA), at the National Gallery, Henry Millon, to work as predoctoral research assistants for the Architectural Drawings Advisory Group, an international consortium convened at CASVA and supported by the J. Paul Getty Trust to set standards for the scholarly cataloguing of architectural drawings online. This early experience in working with an international group of scholars on one of the first electronic database projects in the history of art stimulated my life-long dedication to advancing the development of electronic tools for art historical research—one that I brought to the Yale Center for British Art when I became director.
The collective of fellowship programs in art history across the museums and research institutes of Washington, DC offered me a rich community of peers as an advanced graduate student and young professional, and this stimulating environment furthered my interest in working within the context of a study center, which had begun at Yale. The appeal of funding art historical research (and research in the humanities more generally) through grants and fellowships was strengthened by the work of my husband, Jack Meyers, an assistant director in the Research Division at NEH at that time—and we have been most fortunate to have developed comparable careers in this regard. While I worked for fourteen years as the Curator of the Virginia Steele Scott Gallery of American Art at the Huntington, which is one of the largest residential fellowship-granting research institutes in the humanities in the world, Jack served as a program officer and then deputy director of the Getty’s Grant Program (now Foundation). We both became fully committed to the support of scholarship internationally, and, over the last years, while I have served as director of the Yale Center for British Art, and CEO of the Paul Mellon Centre for Studies in British Art (PMC) in London, Jack has served as President of the Rockefeller Archive Center. Our complementary positions have allowed us to share our experiences in the running of study centers, which has been wholly gratifying, and, I hope, of benefit to our mutual institutions.
JTP: What would you say are some of the biggest changes you’ve seen during your time at the YCBA?
AM: Certainly the greatest change I have seen in the field of British art over the last seventeen years, which has affected the YCBA and PMC in fundamental ways, and to a certain extent has been promoted by these sister institutions, has been a major shift in vantage point from what commonly has been called the “imperial gaze” to a more global viewpoint. Although by the time I was named director of the YCBA seventeen years ago, the approach to British art had become as much concerned with social history as with connoisseurship, works still were interpreted largely in terms of a relatively closed history of European art. The complex and tragic histories of the British Empire and slave trade were only beginning to affect the ways in which British art was understood, and the canon remained essentially defined as the creation of white, male artists of British birth—or, more generously, of white, male European or colonial American artists who came to practice in the British Isles, or who were associated with British artists and patrons on the Grand Tour.
Over the last years, a sea change has taken place, and not only has the canon expanded—and shifted—to include works by artists from many other parts of the world that came under British dominion or were deeply affected by the Empire, but also by artists of more diverse racial backgrounds and genders. The sense of the West’s ownership of the world on the part of historians of British art has been altered dramatically, and standard practice now insists that even the most traditionally canonical works must be reinterpreted from a global vantage point, and in terms of much larger and more challenging histories.

Art and Emancipation in Jamaica: Isaac Mendes Belisario and his Worlds, curated by Tim Barringer, Gillian Forrester, and Barbaro Martinez Ruiz, Yale Center for British Art, 2007, photo by Richard Caspole
JTP: What is a favorite memory—perhaps one that is less well-known—from your time there?
AM: My fond memories from my years at the YCBA—and the PMC—are innumerable, and it is extremely difficult to select a favorite. However, one program stands out as particularly memorable for me personally. In July of 2005, the YCBA co-organized a conference entitled, “Ways of Making and Knowing: The Material Culture of Empirical Knowledge,” with the PMC and the Wellcome Trust Center/Centre for the History of Medicine at University College London (UCL).

Pamela Smith, Harold Cook, and Amy Meyers, standing in front of a raised flower bed reconstructed from an eighteenth-century plan by garden historian Mark Laird, at Painshill Park, in Cobham, Surrey, during the final session of “Ways of Making and Knowing: The Material Culture of Empirical Knowledge,” July, 2005.
My co-conveners were close associates in the history of science: Pamela Smith, who is the Seth Low Professor of History at Columbia University, and Harold Cook, who, at that time, was director of the Wellcome Trust Center and now is the John F. Nickoll Professor History at Brown University. Beginning with a series of discussions at the Huntington, we planned an interdisciplinary conversation about the material construction of knowledge, examining how artisans and other makers of things informed the ways in which the natural world came to be understood in the West, from the sixteenth-century through the nineteenth. Exploring the relationship between two spheres traditionally understood to be distinct—practical and theoretical knowledge, the lectures and demonstrations were given by the seventy presenters, including art historians and historians of material culture, historians of science, artists, and craftspeople.
The program took place over five days, at sites across London ranging from the Chelsea Physic Garden, the Enlightenment Gallery at the British Museum, the Royal Botanical Gardens at Kew, the Natural History Museum, the Linnean Society, the V&A, and Painshill Park, in Surrey. This experimental program included as many object-study sessions and hands-on making workshops as formal papers, interrogating how the use of natural materials in the processes of making yielded the most profound understanding of nature, feeding science as much as technical knowledge in exciting new ways. A selection of the papers appeared under the title of the conference, in the Bard Graduate Center’s series Cultural Histories of the Material World, published by the University of Michigan Press in 2014. I must say that the support of Brian Allen, at that time the splendid and long-serving Director of Studies of the PMC with whom I had the honor of working closely for ten years, was a special pleasure.
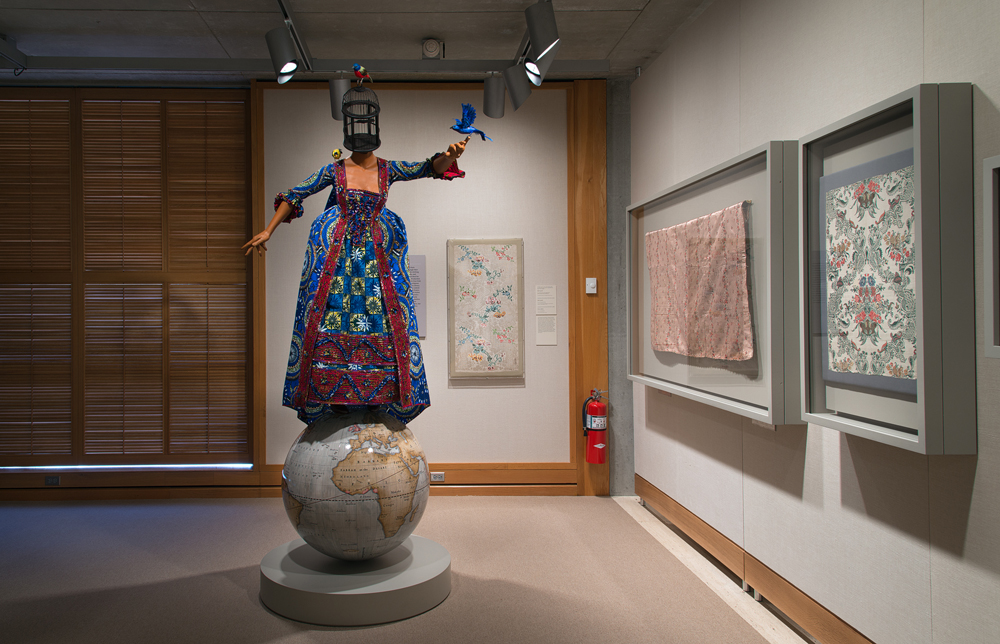

Enlightened Princesses: Caroline, Augusta, Charlotte, and the Shaping of the Modern World installation, including Yinka Shonibare CBE’s Mrs Pinckney and the Emancipated Birds of South Carolina (2017), Yale Center for British Art, photo by Richard Caspole
I also remember with great fondness working with Joanna Marschner, Senior Curator at Kensington Palace, on Enlightened Princesses: Caroline, Augusta, Charlotte, and the Shaping of the Modern World, an exhibition co-organized by the YCBA and Historic Royal Palaces, with the support of the PMC, that was mounted in New Haven and London in 2017. Our mutual interest in women and patronage, particularly in relation to the natural sciences, found its expression in this project, and we look forward to working together on the subject long into the future.
JTP: What is a resource at the YCBA that you think people don’t often know about, but should?
AM: The collection of British art at the YCBA is renowned as the largest and finest outside the UK, comprising over 2,000 paintings; 20,000 drawings and watercolors; 45,000 prints and photographs; and several hundred pieces of sculpture. Much less well known is the institution’s truly glorious rare book and manuscript collection. The Center’s founder, Paul Mellon, began his life as a collector in this field, and over his lifetime he amassed one of the greatest collections formed in the twentieth century, comprising approximately 35,000 titles. Mr. Mellon focused in part on British illustrated books, acquiring the renowned J.R. Abbey collection of British color plate books, which serves as the touchstone for all other collections of this kind. Other major parts of the collection include drawing manuals, sporting books and manuscripts, early maps and atlases, early printed books by Caxton and his contemporaries, and archival and manuscript material relating to British artists, writers, and travelers of all periods.
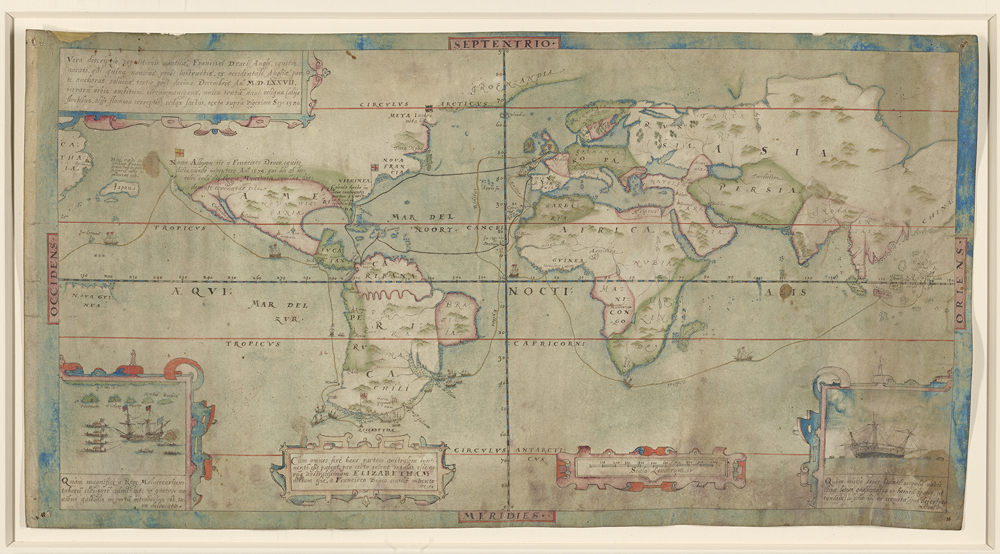
A True Description of the Naval Exploration of Francis Drake, Englishman & Knight, Who With Five Ships Departed from the Western Part of England on 13 December 1577, Circumnavigated the Globe and Returned on 26 September 1580 with One Ship Remaining, the Others Having been Destroyed by Waves or fire, [London (?), ca. 1587], pen and ink and watercolor on parchment, Yale Center for British Art, Paul Mellon Collection
The Rare Books and Manuscripts collection contains splendid photographic holdings, beginning with some of the earliest printed books including original photographic illustrations produced by the first British experimenters with paper-print photography, such as William Henry Fox Talbot. These collections have grown enormously over the years, as have the photographic collections in the Prints and Drawings Department, making the Center one of the most significant repositories of British photographs in the country.
The same holds true for the development of the institution’s collection of contemporary British art, and over the course of this summer, the Center has mounted an exhibition illuminating the role that donors have played in enhancing both areas of the institution’s collections over the last few years. Entitled Photographs/Contemporary Art: Recent Gifts and Acquisitions, the exhibition demonstrates the breadth and depth of these holdings and signals their continued growth.
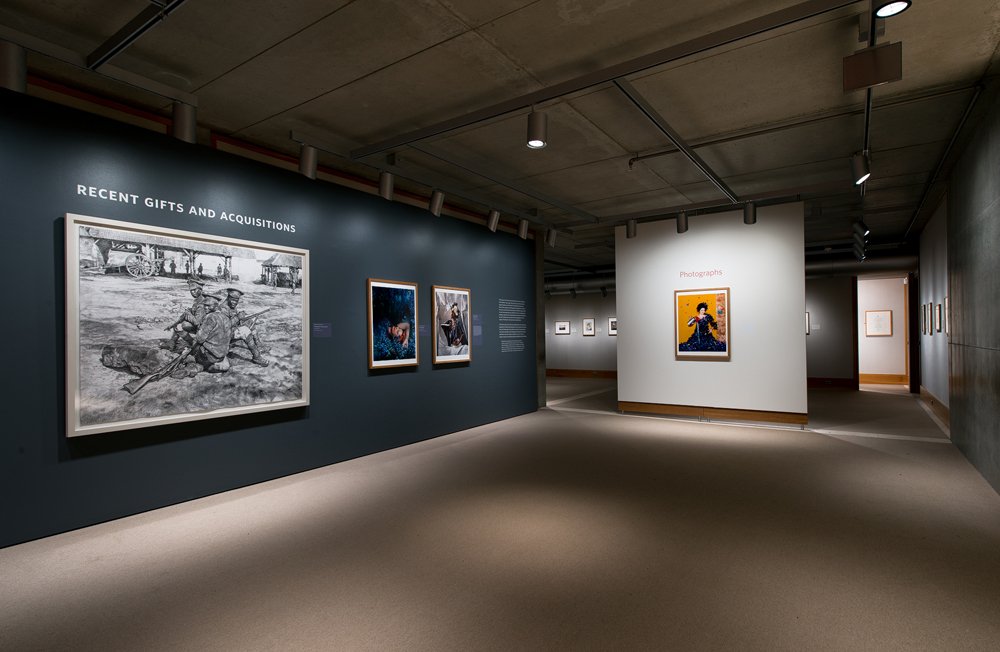

Photographs | Contemporary Art: Recent Gifts and Acquisitions installation, Yale Center for British Art, photo by Richard Caspole
JTP: When did you first become a CAA member? Do you have a favorite memory from a CAA conference?
AM: I have been a member of the CAA for so long that I do not remember precisely when I joined—undoubtedly by the early 1980s, when I was attending conferences regularly in my later years of graduate school. My memories of the very first conference I attended are shrouded in the mists of time, but I believe that I joined a group of Yale graduate students at a conference in New York while I was still enrolled in courses, in the late 1970s.
I have countless happy memories from conferences throughout the years, from sessions I have co-organized on the visual and material culture of natural history with my long-standing colleague, Therese O’Malley, to the multitude of fine papers given by scholars in my own fields of American and British art. Of course, one of the most important functions of the conference is to introduce participants to subjects that lie beyond their own areas of expertise, and I have learned an enormous amount from papers on topics to which I have had little exposure, especially as art history has evolved in such exciting ways over the last years. New methodological approaches are always stimulating to consider, and I particularly have enjoyed learning from the work of younger colleagues. Indeed, the call for papers for next year’s conference promises a rich and important group of sessions that will have me running from one talk to the next throughout the proceedings.
Since 1989, due to my association with The Huntington and the YCBA and PMC, I have had the pleasure of attending the winter meeting of the Association of Research Institutes in Art History (ARIAH), as an affiliated society, which always is held the first day of the CAA conference. Naturally, I also have enjoyed attending reunions of the departments and study centers with which I have been connected. The joint reunion of the YCBA and PMC has been a true pleasure to co-host with the PMC’s current Director of Studies, Mark Hallett, who promotes the mutual interests of his London research center and the YCBA with dedication and inspired vision. Mark and I have been deeply grateful to the Deputy Directors of Research of these sister institutions, Martina Droth and Sarah Turner, for organizing these shared events annually.
I do have one favorite memory that stands out among all others, however, and that is of the 2009 Terra Foundation for the Arts Distinguished Scholar Session, entitled “Generations: Art, Ideas, and Change,” in honor of Jules Prown. Chaired by Bryan Wolf, and including papers by Alex Nemerov, Margaretta Lovell, Jennifer Roberts, Jennifer Greenhill, and Ethan Lasser, the session paid special tribute not only to the professor who had inspired so many of us as graduate students at Yale, but also to the scholar who had informed the work of students pursuing the study of American art and material culture throughout the world through his groundbreaking research and approaches to analysis.
JTP: I imagine it is impossible to summarize the sentiments surrounding a 17-year tenure, but if there was one feeling you could share in the wake of your departure from the directorship of the YCBA, what would you say it is?
AM: The feeling I wish to share is one of excitement.

Courtney J. Martin, photo by Argenis Apolinario
As I have indicated, the field of British art–and of art history more generally—is developing and changing in such important ways, and I have no doubt that Courtney J. Martin, who just has begun her first term as the Center’s brilliant new director, will work with her YCBA colleagues not only to continue to introduce the work of new artists to the collection, but to encourage an ever-expanding community of visitors from the university, the city, the region, and the world through innovative displays, exhibitions, publications, and programs. She is a tremendous addition to the impressive complement of collection directors under the excellent leadership of Yale’s Vice Provost for Collections and Scholarly Communications, Susan Gibbons, and I expect that splendid developments are about to take place across all of the university’s museums and libraries with this gifted team in place.
JTP: What are you most proud of having accomplished at YBCA?
AM: My pride lies in what I was able to accomplish in concert with my superlative friends and colleagues: the staff of the YCBA and PMC, Yale students and faculty members, the 250 visiting scholars who have joined our community to pursue research in the YCBA’s collections, our advisory committees and consultants, the PMC’s Board of Governors, and supporters of both institutions. So much has been accomplished collectively that a full review would be impossible, but I will outline some of our most significant collaborative achievements.
Working with museums and cultural institutions across the UK, and in certain instances the United States, we developed a program of over fifty major loan exhibitions which explored a wide range of topics from the early modern period through the current day. These were underpinned by workshops involving students and scholars from around the world, and they were enhanced by an equivalent number of significant publications produced in association with Yale University Press London (YUPL). Approximately forty in-house exhibitions and displays, often developed with undergraduates and graduate students, enriched the exhibition program, examining the Center’s own holdings from important new vantage points.
One such exhibition, Unto This Last: Two Hundred Years of John Ruskin, curated by three of Tim Barringer’s graduate students—Tara Contractor, Victoria Hepburn, and Judith Stapleton—has been in the planning stages for some time as the Center’s central contribution to the bicentennial commemoration of Ruskin’s birth (both critical and celebratory), and it will open on the evening of September 17th of this year, accompanied by a leading-edge catalogue edited by Tim, to which the students, and others, have contributed. I have no doubt that for this cohort of students, the experience of working with Tim on an assessment of Ruskin’s significance as a thinker for the modern world will be as important as George Hersey’s Ruskin seminar was for me and my own group of peers over forty years ago.
During the last seventeen years, the research cultures of the YCBA and the PMC were augmented through the joint efforts of a new Research Division at the Yale Center and an amplified program at the London Centre, which also produced a superb run of publications with YUPL. Support of scholars across the field of British art was substantially increased through the PMC’s grant program and the YCBA’s visiting scholars program. The PMC and YCBA also collaborated to develop an innovative online journal, British Art Studies, which is fully accessible, free of charge, to the world.
The YCBA’s education program developed magnificently, as well. Our docents toured 92,929 school-age students through the galleries, and an average of 88 Yale classes utilized the collections each year, with nearly 14,000 Yale students visiting the Study Room either with a class or to use collections on their own. The Center hosted 903 undergraduate student interns and workers, 76 graduate student research assistants, and 20 postdoctoral research associates who received doctorates from other universities. Empirically based programs focused on close looking in the galleries, designed to increase both the sensitivity and diagnostic skills of medical and nursing students (the first such programs in the world), continued to develop for Yale graduate student in other fields.
Additionally, creative learning programs for teenage girls on the autism spectrum were put into place, and a teaching relationship with Chapel Haven, a home for adults with cognitive disabilities, flourished. The Center actively joined the university’s mentorship program to engage undergraduates who have attended New Haven public schools, or approved charter schools, and who have been awarded New Haven Promise scholarships, in professional experiences over the summer months. We benefitted from the fine work of those who were participants in the program, and we were able to add several extremely talented young people to our permanent staff from the program.
The collections also developed in exciting ways over the years, with curators adding to the historic corpus with important works from the Tudor period through the mid-twentieth century, and with modern and contemporary works expanding the Center’s holdings into our own time.

Fourth-floor gallery installation, including the new acquisition of Peter Lely’s Diana and her Nymphs at a Fountain (ca.1648), Yale Center for British Art, photo by Edward Town
Sculpture became a special focus of the acquisitions program, along with photography and modern and contemporary art. In all, almost 9,000 objects and collections across the curatorial departments amplified the Center’s holdings for teaching, research, and exhibition.
A program to make the Center’s entire collection accessible virtually, placed 90,000 records online, and 78,000 high-resolution digital images of works in the public domain freely available to the world for any use, in concert with Yale’s Open Access policy. The Center now seeks to connect these online collections with others across the university and the globe, through linked open data, allowing audiences worldwide to explore the rich global history of British art.
We also worked with collections across the university to develop a state-of-the-art conservation program on Yale’s West Campus, and to create the Institute for the Preservation of Cultural Heritage, with a major conservation science program intended not only for the technical assessment of our own collections, but also to address global conservation needs. Additionally, the Center published a model conservation plan for its landmark building designed by Louis I. Kahn, which has helped to steer the conservation of other modern buildings of cultural significance according to best practices. This plan allowed a three-phased conservation program to address the physical needs of the Kahn building, and following the conservation of the interior spaces and upgrading of the mechanical systems, a freshly conceived display of the art collections was installed, entitled “Britain in the World.”
JTP: What are you most excited about when you think of your next steps? Are there projects you are looking forward to?
AM: Returning to my own scholarship is a great joy, and I am beginning to work with Therese O’Malley to co-curate an exhibition examining the naturalists John and William Bartram and the early development of environmental thought in North America and the transatlantic world—a project that derives from the dissertations on which we worked together so many years ago, but that now is informed by the scholarship of those working on the culture of natural history in the Americas from new points of view.

William Bartram, The Soft Shell’d Tortoise Got in Savanah River Georgia, ca. 1773, gray wash, pen and black ink, and graphite on paper, Yale Center for British Art, Gift of Charles Ryskamp
The Bartrams, who created one of the first scientific gardens in the British colonies, began to be mythologized in their own time, and have been the focus of academic study since the nineteenth century. However, their work is just beginning to be assessed in relation to the knowledge they gained not only from Native American peoples they encountered on their collecting expeditions, but from enslaved peoples of African descent in bondage to the Bartrams’ family members and friends throughout the southern colonies, as well as those William himself enslaved on a small, short-lived plantation that he attempted to establish in Florida. This project will serve as a case study examining the diverse systems of knowledge about nature that converged and collided in this period, resulting in new conceptions of a wholly interconnected cosmos, in a constant state of flux.
Amy Meyers BIOGRAPHY
Amy Meyers (Yale PhD, American Studies, 1985) retired from the directorship of the Yale Center for British Art on June 30th of this year. Prior to her appointment in July of 2002, she spent much of her career at research institutes, including Dumbarton Oaks; the Center for Advanced Study in Visual Arts at the National Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C; and The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens, where she served as Curator of American Art from 1988 through June of 2002. Meyers also has taught the history of art at the California Institute of Technology, the University of Michigan, Mount Vernon College, and Yale. As Director of the Center, Meyers sought to strengthen the institution’s educational and research initiatives. She endeavored to promote a rigorous academic publication program in association with Yale University Press and to develop an exhibition program of the highest scholarly standard in partnership with major museums across Europe and the United States. She expanded the Center’s fellowship program; amplified the teaching mission in concert with departments and programs across the university; and promoted the cataloguing of the collections on-line, with free and open access to all images in the public domain. Meyers supported the creation of a conservation plan for the institution’s landmark building, designed by Louis I. Kahn, and she oversaw the conservation of the building, as well as two full-scale reinstallations of the entire collection.
Meyers has written extensively on the visual and material culture of natural history in the transatlantic world, serving as editor of Knowing Nature: Art and Science in Philadelphia, 1740 to 1840, with the assistance of Lisa Ford (New Haven: Yale University Press, 2011); with Harold Cook and Pamela Smith, Ways of Making and Knowing: The Material Culture of Empirical Knowledge (Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan Press, 2011); with Therese O’Malley, The Art of Natural History: Illustrated Treatises and Botanical Paintings, 1400-1850 (Washington, D.C.: National Gallery of Art, Studies in The History of Art Series, 2008); Art and Science in America: Issues of Representation (San Marino: The Huntington, 1998); and, with Margaret Pritchard, Empire’s Nature: Mark Catesby’s New World Vision (Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 1998). She also has organized numerous international symposia in the field, including Curious Specimens: Enlightenment Objects, Collections, Narratives (with Luisa Calè, Michael Snodin, Margaret Powell, and Cynthia Roman; London, 2010), Ways of Making and Knowing: The Material Culture of Empirical Knowledge (with Hal Cook and Pamela Smith; London, 2005); and ‘Curious in Our Way’: The Culture of Nature in Philadelphia, 1740 to 1840 (Philadelphia, 2004). With Therese O’Malley, she currently is co-organizing an exhibition on John and William Bartram and the emergence of an environmental conception of the natural world in colonial and early republican America, to be mounted in 2024.





