CAA News Today
Petition to Support University Galleries and Museums
posted by CAA — July 14, 2009
Several university art museums or their school administrations have recently sold, or have attempted to sell, artworks and objects in their collections to offset operating costs. In response to this, CAA has joined a task force supporting the educational importance of preserving collections at university museums and galleries. The task force—which includes representatives from the American Association of Museums, the Association of Art Museum Directors, the Association of College and University Museums and Galleries, and the Samuel H. Kress Foundation—has established a two-pronged effort: 1) to recognize museums as integral educational resources in the university accreditation process; and 2) to heighten public awareness of the educational value of art museum collections.
Members of the task force are meeting with accreditation organizations throughout the country to enlist their support for the recognition of art museums as integral educational resources.
A petition has been prepared that reaffirms the integrity and value of university and college museums.
Please show support for our efforts by adding your name and affiliation to this petition, which will be published in the Chronicle of Higher Education this fall. Please encourage your university, college, or museum to sign it as well.
Thank you for your support on this critical issue.
Paul B. Jaskot, President, and Linda Downs, Executive Director
New Faces for CAA Journals
posted by Christopher Howard — July 10, 2009
Paul Jaskot, president of the CAA Board of Directors, has made new appointments to CAA’s three scholarly journals.
Karen Lang, associate professor of art history at the University of Southern California, has been appointed the next editor-in-chief of The Art Bulletin, succeeding Richard J. Powell of Duke University. Lang begins her three-year term on July 1, 2010, with the preceding year as editor designate.
Michael Cole is the new reviews editor for The Art Bulletin, succeeding David J. Roxburgh of Harvard University, who served the journal for three years. Cole became reviews editor designate in February and took over from Roxburgh this month.
Joining the Art Bulletin Editorial Board for four-year terms beginning July 1, 2009, are: Linda Komaroff, Los Angeles County Museum of Art; Thelma K. Thomas, Institute of Fine Arts, New York University; and Eugene Wang, Harvard University. The newly selected editorial-board chair is Natalie Kampen of Barnard College, who will serve for two years.
At Art Journal, Howard Singerman of the University of Virginia has been appointed the new reviews editor; he will take over from Liz Kotz of the University of California, Riverside, and serve from July 1, 2010, to June 30, 2013, with a year as reviews editor designate starting this month.
Also at Art Journal, Rachel Weiss of the School of the Art Institute of Chicago and Constance DeJong of Hunter College, City University of New York, have joined the Art Journal Editorial Board for the next four years.
Now on the caa.reviews Editorial Board is Michael Ann Holly of the Sterling and Francine Clark Art Institute, who will serve for four years. In addition, seven new field editors for books and related media have been chosen:
- Molly Emma Aitken, City College, City University of New York, South and Southeast Asian art
- Darby English, University of Chicago, contemporary art
- Jonathan Massey, Syracuse University, architecture and urbanism, 1800–present
- Adelheid Mers, School of the Art Institute of Chicago, arts administration and museum studies (a new field-editor position)
- Tanya Sheehan, Rutgers University, photography
- Janis Tomlinson, University Museums at the University of Delaware, Spanish art
- Tony White, Indiana University, Bloomington, artist’s books and books for artists (a new field-editor position)
Field editors work with the journal for three years, starting on July 1, 2009.
All editors and editorial-board members are chosen from an open call for nominations and self-nominations, published in at least two issues of CAA News (usually January and March) and on the CAA website.
Oregon Passes Bill Supporting Part-Time Professors
posted by Christopher Howard — July 06, 2009
Part-time faculty in the state of Oregon scored a victory late last month, when their state legislature overwhelmingly approved the Oregon Faculty and College Excellence (FACE) Act. The bill will provide access to healthcare insurance to part-time faculty at community colleges and universities through the Oregon Educator’s Benefit Board plan. The bill also requires schools to track and annually report on faculty staffing and salary ratios, to be reviewed by the legislature and governor.
The Senate vote was unanimous: 30-0; the House passed the bill 54 to 1. The FACE Act now goes to Oregon Governor Ted Kulongoski for his signature. Jillian Smith and Rob Wagner from AFT Oregon have the complete story.
Faculty and College Excellence (FACE), a branch of the American Federation of Teachers, is a national campaign that advocates for equity in pay and benefits for contingent faculty members through organizing, legislative advocacy, and collective bargaining. Another goal is to ensure that three-quarters of undergraduate courses are taught by full-time tenure and tenure-track faculty, and that qualified contingent faculty have the opportunity to move into such positions when they become available. The Oregon legislation is the first time that elements of FACE have been adopted by a state.
CAA has 135 individual and 21 institutional members in Oregon.
Baruch College Creates Interactive Guide for Teachers Using Copyrighted Materials
posted by Christopher Howard — June 25, 2009
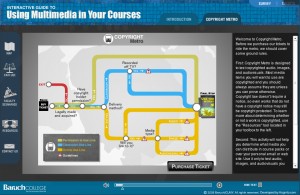 Baruch College of the City University of New York (CUNY), together with Kognito Solutions, has recently released the Interactive Guide to Using Copyrighted Media in Your Courses. This online tutorial helps college and university faculty determine the appropriate guidelines to follow when using different types of copyrighted media in their courses.
Baruch College of the City University of New York (CUNY), together with Kognito Solutions, has recently released the Interactive Guide to Using Copyrighted Media in Your Courses. This online tutorial helps college and university faculty determine the appropriate guidelines to follow when using different types of copyrighted media in their courses.
While US copyright law has traditionally allowed for “fair use” for teachers who display and perform copyrighted media during face-to-face teaching, copyright compliancy has become an increasingly complex legal issue as media are increasingly delivered to students online.
Structured as a subway map, the interactive guide asks teachers a series of questions about the nature of the copyrighted works they want to use and how they plan to use them. As each question is answered, users progress through the virtual subway system, learning important copyright rules that apply to their specific situations. At the “final stop,” a list of guidelines for using the copyrighted media is provided.
John Dugan, legal counsel for Baruch College, said, “This guide is a valuable tool that enables faculty to obtain useful, practical advice on copyright issues they may face without confronting the daunting complexities of the copyright law itself.” Baruch’s assistant vice president for technology, Arthur Downing, who initiated the project, said, “We are responding to the needs of academic institutions for a tool that will help and encourage faculty to use media in their courses. This is especially crucial since higher education is increasingly utilizing technology and online delivery components to augment classroom interaction.”
Downing also noted that, while the new learning resource is based on Baruch College and CUNY copyright guidelines, these guidelines are common to many academic institutions and thus applicable for universities across the nation. He further emphasized the need to “continuously enhance this resource with the help of the educational community.”
Other Copyright Resources
Last summer, CAA launched Intellectual Property and the Arts, its own resource for copyright, digital, and intellectual-property issues related to the visual arts. In addition, Information and Library Services at the University of Maryland University College hosts a webpage with a broad range of information on legally using copyrighted materials in classes and on the internet; this information is especially useful for beginners. Reed College also maintains a simpler webpage on using copyrighted materials in academia, with helpful links to information gathered by other schools and organizations.
Study Finds Overreliance on Part-Time Faculty in Higher Education
posted by Christopher Howard — May 18, 2009
 The primary finding of a report released last week by the American Federation of Teachers (AFT), entitled American Academic: The State of the Higher Education Workforce 1997–2007, presents a troubling picture of disinvestment in the higher-education teaching profession—notably, a reduction in the proportion of full-time tenured and tenure-track faculty, and an increased reliance on employing “contingent” faculty and instructors such as part-time faculty, full-time nontenure track faculty, and graduate employees.
The primary finding of a report released last week by the American Federation of Teachers (AFT), entitled American Academic: The State of the Higher Education Workforce 1997–2007, presents a troubling picture of disinvestment in the higher-education teaching profession—notably, a reduction in the proportion of full-time tenured and tenure-track faculty, and an increased reliance on employing “contingent” faculty and instructors such as part-time faculty, full-time nontenure track faculty, and graduate employees.
An analysis of the most recent ten years of national data finds that the higher-education instructional workforce grew in the past decade, which is not surprising since college enrollments increased during that time by over 3 million. But to meet the needs of a growing student population, colleges and universities overwhelmingly relied on hiring undersupported contingent faculty and instructors. Previous reports have demonstrated the problems created when colleges hire contingent faculty and instructors without fair wages, job security, and professional support. This new report documents that, rather than working to reverse these trends and investing in a more secure higher-education teaching workforce, colleges and universities are expanding their reliance on contingent faculty and instructors.
Among the report’s other key findings:
- From 1997 to 2007, the proportion of full-time tenured and tenure-track faculty members declined from approximately one-third of the instructional staff to slightly more than one-quarter
- The increased reliance on contingent faculty and instructors was found in all sectors of higher education, with the most dramatic increase in community colleges
At the same time, the study notes an increase in the number of professional staff who provide direct student services, such as registrars, counselors, and financial-aid officers. Professional staff grew by 50 percent from 1997 to 2007, and the vast majority of these positions were full-time.
This report is the first in a new series on the higher-education workforce in colleges and universities. Each issue in AFT’s American Academic series will explore different aspects of trends in hiring, compensation, and working conditions among the increasingly diverse higher-education workforce. More higher education data can be found in AFT’s Higher Education Data Center.
The Chronicle of Higher Education and Insider Higher Ed have reported on the report, with extensive comments by readers posted to the latter article.
CAA encourages all colleges and universities to read and uphold its Guidelines for Part-Time Professional Employment, which give recommendations on fair compensation, office and studio space, benefits, and more for part-time workers.
CAA 2009–10 Operating Budget Reductions
posted by Linda Downs — May 11, 2009
Updated May 14, 2009.
Like most universities, art museums, and learned societies, CAA has been significantly affected by the global economic downturn. The Board of Directors made difficult decisions at its May 2009 meeting that nevertheless will allow CAA to maintain the high quality of member services and programming. Strategic reductions and other measures have been instituted throughout the association to balance the budget and keep core programs, publications, and services in operation. With this careful financial planning, CAA remains dedicated to supporting members and the visual-arts community at large through our advocacy, career services, publications, and conference.
Annual Conference
The 2010 Annual Conference in Chicago will commence on Wednesday evening, February 10, with Convocation and the Gala Reception. All 120 planned sessions will be presented over the following three days, Thursday, February 11 to Saturday, February 13, with the addition of extended evening hours. No sessions will take place on Wednesday.
Publications
Newsletter: Beginning July 2009, CAA News will only be distributed online in a new reader-friendly design. This allows us to save printing and mailing costs and help to preserve coverage of core programs and publications. CAA’s website, www.collegeart.org, will become the primary hub of up-to-date information on the organization.
Journals: CAA’s longtime support of the journals is absolutely central to the mission, and the association is fully committed to maintaining them now and in the future. The Art Bulletin and Art Journal will continue to be published. Illustrations, however, will be limited to black and white for 2009–10, except where editorial and budget decisions may allow the insertion of color. caa.reviews will be unchanged, with new book reviews, exhibition reviews, and conference and symposia reports published regularly. While the CAA Board of Directors has determined the budget restrictions necessary for this part of the association, the editors-in-chief will work closely with staff and editorial boards to make sure that any further reductions are implemented with a strict attention to quality consistent with the identity and mission of the journals.
Grants and Fellowships
Two programs in CAA’s grant-making arm will be suspended for 2009–10: the Professional Development Fellowship Program for graduate students and the Millard Meiss Publication Fund. However, the Annual Conference Travel Grants and the Wyeth Foundation for American Art Publication Grant will both continue, and the CAA Annual Exhibitions, also funded by a grant, will take place at the Chicago and New York conferences.
Obama Requests NEA and Arts-Education Budget Increases
posted by Christopher Howard — May 08, 2009
President Barrack Obama has released his budget recommendations for fiscal year 2010, which includes $161.3 million in funding for the National Endowment for the Arts—$6.3 million over the previous year’s budget and the largest increase in fifteen years (about 4 percent). Obama’s administration also requested $38.16 million for the Arts in Education program at the US Department of Education.
CAA encourages you to contact your legislators to voice your support for these increases in arts and cultural funding through the Arts Action Center, sponsored by Americans for the Arts. You can use or modify existing letter templates to tell Congress to support Arts in Education and the National Endowment for the Arts.
Spring Art Journal Published
posted by Christopher Howard — May 04, 2009
 In her introductory editor’s letter to the recently published Spring 2009 Art Journal, Judith Rodenbeck underlines the notion of retooling in the issue. The authors and contributors, she notes, confront three areas in particular: how the expansive global art world thrives in non-Western countries; how art education is undergoing progressive change outside traditional art academia; and how a history of early computer art can inform contemporary practice.
In her introductory editor’s letter to the recently published Spring 2009 Art Journal, Judith Rodenbeck underlines the notion of retooling in the issue. The authors and contributors, she notes, confront three areas in particular: how the expansive global art world thrives in non-Western countries; how art education is undergoing progressive change outside traditional art academia; and how a history of early computer art can inform contemporary practice.
Gail Gelburd’s essay, “Cuba and the Art of ‘Trading with the Enemy,’ ” looks at Cuban-American relations over the past fifty years and their effect on cultural exchange. In her essay “Urban Claims and Visual Sources in the Making of Dakar’s Art World City,” Joanna Grabski discusses the Dak’Art Biennale in relation to Senghorian Négritude, the city’s School of Fine Arts, and Dakar’s urban fabric.
During the past several years, Art Journal has investigated retoolings in pedagogical issues. “The Currency of Practice: Reclaiming Autonomy for the MFA,” developed from a roundtable discussion that took place at the CAA Annual Conference in 2007, explores alternatives to traditional graduate degrees such as often-nomadic, nonaccredited schools, organizations led and run by artists, and programs for PhDs for artists.
Moving forward by looking back, three essays explore the history and practice of digital art. The artist Paul Hertz presents an overview that draws on his recent cocurated exhibition, Imaging by Numbers: A Historical View of the Computer Print. A computer scientist and pioneering artist, Frieder Nake, examines early European computer artists and their work, which he calls “algorithmic images accepted as art.” Patric D. Prince, a scholar, artist, and collector of computer art, provides a short history of computer-generated imagery and digital printmaking in America before the era of the home computer.
Reviews include texts on recent projects by Boris Groys (a collection of essays and an exhibition) and a book on Marcel Duchamp and artists’ labor. Letters to the editor include two replies to an Art Journal article, “Steps to an Ecology of Communication: Radical Software, Dan Graham, and the Legacy of Gregory Bateson,” from the Fall 2008 issue.
Rose Board Responds to Museum Crisis
posted by Christopher Howard — April 24, 2009
The board of overseers at the Rose Art Museum at Brandeis University released a statement yesterday, found here and here, to counter provost Marty Wyngaarden Krauss’s missive from last week about keeping the building open to art exhibitions beyond this summer. Since late January, when the university first announced plans to close the museum and sell its collections, the school administration has backpedaled several times, claiming to transform the museum into an art study and exhibition center (which it already is), to not sell the entire collection, and to continue hosting exhibitions. To which the board responds:
In her letter, Krauss attempted to clarify future plans for the Rose Art Museum once the University closes it on June 30, 2009. Despite the existence of the current Board of Overseers for the museum, Brandeis has named a new committee to “explore future options for the Rose.” In addition, the current position of museum director will be eliminated. According to Jon Lee, chair of the Rose Art Museum’s Board of Overseers, “Without a director or curator, the Rose cannot continue to function as a museum under any meaningful definition. Since the University’s announcement on January 26, 2009 that it would close the museum, membership and Rose Overseer dues, and all donations have ceased or been asked to be returned. This amounts to more than $2.5 million.”
“When the Rose family originally founded the Rose Art Museum, they were very clear about its mission and the integral role it would play as a part of the Brandeis community,” said Meryl Rose, a member of the Rose Art Museum’s Board of Overseers and a relative to the original museum founders. “A museum with a collection and reputation such as the Rose needs a director, and while Krauss’s letter states that the collection will be cared for, it does not erase the fact that the Rose as we know it will cease to exist under the administration’s current plans. The administration is carrying out an elaborate charade, the first step of which is to turn the Rose from a true museum as its founders intended, into something quite different….”
Again, the full statement can be found here and here. Richard Lacayo, art and architectural critic for Time, wrote about Brandeis’s announcement last week and quotes Rose director Michael Rush:
So long as the Rose remains open as a museum, it remains subject to the ethical guidelines of American museum groups that do what they can to discourage the kind of emergency sales that Brandeis is contemplating. But I spoke later with Michael Rush, the director of the Rose, who will soon be gone, along with several other significant Rose staffers. He was skeptical about what the university was doing. “They’re talking about keeping the Rose open,” he said. “But there’s no director, no curator, no education director, no funding stream and no program.”
An update to Lacayo’s report is a message from Jon Lee, Rose board chairman, which notes that Massachusett’s Attorney General office is watching developments closely.
The situation at Brandeis is one of many taking place concerning unusual uses of restricted endowments and related funding. In his article “New Unrest on Campus as Donors Rebel,” John Hechinger of the Wall Street Journal writes, “As schools struggle more than they have in decades to fund their core operations, many are looking to a rich pool of so-called restricted gifts—held in endowments whose donors often provide firm instructions on how their money should be spent.”
Read more of CAA’s coverage of the Rose Art Museum. The museum itself has been keeping a comprehensive log of articles and reviews.
Rose Art Museum to Remain Open, with Uncertain Future
posted by Christopher Howard — April 17, 2009
The website of Art in America magazine reports that the Rose Art Museum is not closing this summer as previously expected: “Current exhibitions—‘Saints and Sinners’ and ‘Hans Hofmann: Circa 1950’—will remain on view through May 17th; after a brief de-install, the museum will re-open on July 22nd with works from the permanent collection.” Four museum staff members are expected to retain their positions, although Michael Rush will no longer direct.
Further, according to the museum administrator Jay Knox, Brandeis University plans to dissolve the museum’s board of directors, and the longterm stability of the collection is still unknown.


