CAA News Today
CIHA World Congresses in Florence and São Paolo
posted by CAA — May 20, 2019
A SESSION AT THE 2019 CAA CONFERENCE INTRODUCED TOPICS FOR The 35th World Congress, Parts 1 and 2, of the Comité International d’Histoire de l’Art (CIHA)
David Roxburgh, Prince Alwaleed Bin Talal Professor of Islamic Art History at Harvard University, contributed the following article about the next two world congresses organized by CIHA so that CAA members can consider attending and participating. Professor Roxburgh is the current president of the National Committee for the History of Art (NCHA), the US affiliate of CIHA that connects the international committee’s work with CAA and its members to sustain the global exchange of art historical work.
Motion: Transformation and the Life of Artworks, the session sponsored by NCHA at the 2019 CAA Annual Meeting in New York, brought together scholars from the organizing committees of Italy and Brazil who will share the quadrennial 35th CIHA World Congress. The themes are Motion: Transformation, taking place in Florence in 2019, and Motion: Migrations, taking place in São Paolo in 2020. The CAA panelists comprised Marzia Faietti (Gallerie degli Uffizi, Florence), Claudia Mattos Avolese (Universidade Estadual de Campinas, São Paulo), Marco Musillo (Kunsthistoriches Institut, Florence), and Christina Strunck (Friedrich-Alexander-University, Erlangen-Nürnberg), with Jesús Escobar (Northwestern University) serving as respondent and Nicola Courtright (Amherst College) as chair. The thoughtful remarks of Professor Jesús Escobar are included here for those who could not attend the panel.
The CIHA Congress in Florence will be held September 1-6, 2019, and in São Paulo September 13-19, 2020. The final program for Florence is now available.
For the São Paulo program, a call for paper submissions is available here.
NCHA recently awarded 12 travel grants to graduate students from PhD programs in the history of art from across the United States to attend the 35th CIHA Congress in Florence. A competition will be announced early in 2020 for graduate students planning to attend the CIHA Congress in São Paulo. We hope to see many art historians working in the US in Florence and São Paulo.
International Review: Opening of the Jameel Arts Centre, Dubai, United Arab Emirates by Sabrina DeTurk
posted by CAA — March 21, 2019
The following article was written in response to a call for submissions by CAA’s International Committee. It is by Sabrina DeTurk, associate professor, College of Arts and Creative Enterprises, Zayed University, Dubai, United Arab Emirates.

Fig. 1: Exterior of Jameel Arts Center, Jaddaf Waterfront, Dubai, UAE. Photo by Sabrina DeTurk.
In November 2018, Dubai witnessed the opening of the Jameel Arts Centre, the city’s first non-commercial contemporary arts space (Fig. 1). Located on the banks of the Dubai Creek, in the still-developing area of the Jaddaf Waterfront, the center is a project of the Saudi-based organization Art Jameel, a foundation focused on arts and culture programming that is sponsored by the Jameel family. The Jameel Arts Centre will be programmed as a kunsthalle, featuring temporary exhibitions showcasing works drawn from the Jameel collection as well as commissioned works by contemporary artists and those on loan from other institutions. Community events and educational outreach are also key elements of the center’s programming initiatives and the 107,640 square-foot space includes facilities such as an open-access library of over 3,000 volumes as well as coworking areas. There will also be a sculpture park as well as an outdoor arena for performing arts or film screenings.
The Jameel Arts Centre’s inaugural exhibitions included a series of artist’s rooms featuring the work of women artists from the Middle East whose work has garnered critical acclaim though not always international visibility. Maha Al Malluh (Saudi Arabia), Mounira Al Solh (Lebanon), Lala Rukh (Pakistan), and Chiharu Shiota (Japan) showed work that reflected on the personal, communal, and political, sometimes all in one piece.
In Maha Al Malluh’s sculpture, Food for Thought, dozens of well-used cooking pots of all sizes are affixed to two walls of the gallery with their undersides facing the viewer. The burns, scrapes and dents on these surfaces become both a pattern and a portrait, suggesting the many meals, large and small, cooked and served in these vessels. The pots invoke both an individual and collective activity of dining. One senses that these pots have traveled far to reach their current destination, perhaps reflecting the experience of refugees who have fled from so many troubled parts of the region, often with few possessions other than simple cooking utensils and basic clothing.
Lala Rukh’s minimalist and meditative prints and video speak to the personal experience of her mother’s death as well as the changing political landscape of Southeast Asia in the 1990s. However, the darkness of the room in which the works are displayed made it all but impossible to read the contextualizing and interpretive materials that are necessary to understand the meaning of Rukh’s subtle forms.

Fig. 2: Installation view of Chiharu Shiota, Departure (2018). Photo by Sabrina DeTurk.
The inclusion of a sculptural installation by Chiharu Shiota, featuring an Arabian dhow (sailing vessel) sourced from a local boatyard, struck an odd note among the rooms (Fig. 2). While Shiota’s sculpture, which featured her signature webs of red yarn, was visually compelling, there was little sense, beyond the inclusion of the local boat, of its contribution to the larger dialogues encouraged by the exhibitions. In an image-obsessed city such as Dubai, one can’t help but wonder if this installation served more as an Instagrammable photo opportunity than as a work of serious contemporary art.
The inaugural group exhibition at Jameel Arts Centre, Crude, was curated by Murtaza Vali and featured the work of eighteen artists and artist collectives. In the show’s catalogue, Antonia Carver, the Director of Art Jameel, described the exhibition as “presenting an innovative material reading of a substance so crucial in shaping local and regional histories and cultures.” The included works run the gamut from archival photographs to video to sculptural installations to found objects and reflect a diversity of artistic approaches to the cultural, political, and economic significance of oil in the region throughout the last six decades.

Fig. 3: Houshang Pezeshknia, Portrait d’homme (1949). Photo by Sabrina DeTurk.
The earliest works in the show, documentary photographs by the Iraqi, Latif Al Ani, and paintings by the Iranian, Houshang Pezeshknia (Portrait d’homme, 1949, Fig. 3), highlight the role that the discovery of oil played in shaping the modern culture and identity of both countries. Al Ani’s photographs focus on the material benefits of the oil industry, featuring images of new, modernist housing developments and smiling children showing the bottles of milk now provided as part of the government school lunch program. Pezeshknia’s paintings are more introspective; their rough brushstrokes emphasize the harsh features of those who work on the pipelines and the scars left on the Iranian landscape by the new technologies of oil extraction.
Several artists in the exhibition drew on found images and archival film footage for their works. These include Raja’a Khalid, whose Desert Golf series (2014) uses vintage print media from American publications such as Life magazine to document the seemingly inexorable, if equally inexplicable, compulsion that expatriate oil executives had for finding ways to play golf in the hostile desert landscape. In several of these images, bewildered local residents look on, setting up an us/them dichotomy and pervasive sense of cultural difference that still marks expatriate and local relations in the Gulf region.

Fig. 4: Installation view of Crude exhibition. Monira Al Qadiri, Flower Drill (2016) is on the wall. Photo by Sabrina DeTurk.
Sculptural installations featured prominently in the exhibition. For example, Monira Al Qadiri’s Flower Drill (2016, Fig. 4), displayed high on the wall in one of the galleries, features fiberglass forms based on the design of drill heads and coated in two-toned automotive paint, connecting the work to both the initial and final stages of oil production and consumption. Alessandro Balteo-Yazbek’s Last Oil Barrel is a tiny wooden sculpture of a barrel, whose price is linked to oil futures and whose value will be determined only at some unspecified date in the future when a sale is fixed, reflecting the connections between the commodity value of both art and oil. The artist identifies the date of the work as “postponed,” indicating that it remains in some way incomplete until that time.
Although Crude was an intellectually rigorous and aesthetically compelling first exhibition from the Jameel Arts Centre, it remains to be seen whether there will be a sufficient audience for this type of show in Dubai over the long term. While the center’s opening weekend saw packed galleries, a weekday in January found the author almost alone in the spaces. The question of representation and inclusion of Emirati artists will undoubtedly also be raised at some point in the center’s development.

Fig. 5: Installation view of Crude exhibition. Hassan Sharif, Slippers and Wire (2009) is in the foreground. Photo by Sabrina DeTurk
A sculpture by the pioneering Emirati conceptualist artist Hassan Sharif (Fig. 5) was included in Crude and works by Emirati sculptors Shaikha Al-Mazrou and Mohammed Ahmed Ibrahim were shown in the lobby and outside garden respectively. However, this is but a small sample of the variety of contemporary art being produced in the United Arab Emirates and local artists may, understandably, begin to call for greater visibility in this high-profile contemporary arts space. The Jaddaf Waterfront remains under construction and as yet there is not a sustained community to support the idea of the Jameel Arts Centre thriving as a local creative hub. That said, the potential for growth and development is there and the openness with which the center is positioning itself is welcome in a city where the arts scene can often feel closed and difficult to penetrate. Jameel Arts Centre is a welcome addition to the creative landscape of Dubai and will hopefully continue to develop as a space for contemporary expression.
International Review: Gordon Walters: New Vision by Leonard Bell
posted by CAA — December 06, 2018
The following article was written in response to a call for submissions by CAA’s International Committee. It is by Leonard Bell, professor of art history, University of Auckland, New Zealand.
Exhibition and catalogue review: Gordon Walters: New Vision, Dunedin Public Art Gallery, 11 November 2017- 8 April 2018, and Auckland Art Gallery, 7 July – 4 November 2018.
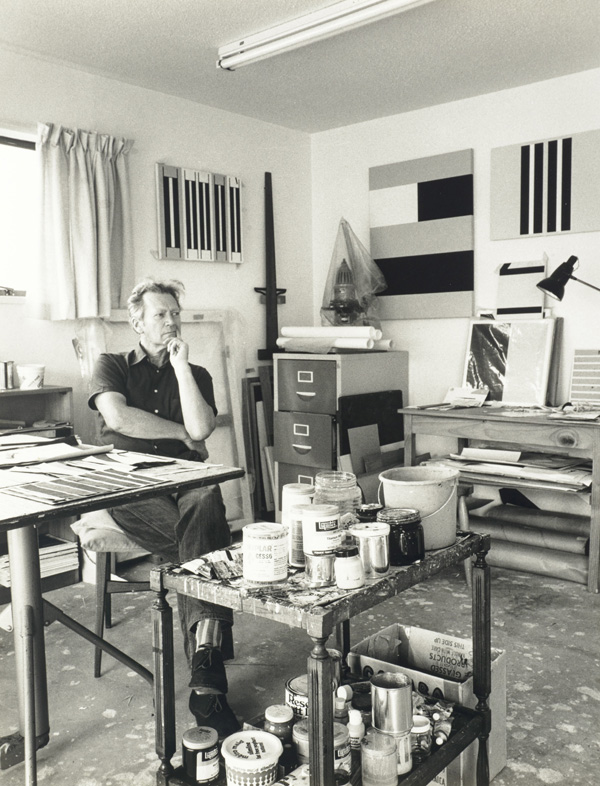

Marti Friedlander, Portrait of Gordon Walters in His Studio, 1978, Marti Friedlander Archive, EH McCormick Research Library, Auckland Art Gallery Toi o Tāmaki, Courtesy Gerrard and Marti Friedlander Charitable Trust.
The much-lauded work of Gordon Walters (1919-1995), one of New Zealand’s first geometric abstract painters, has also generated controversy. A retrospective show traveled the country in 1983, but the present exhibition is the first comprehensive survey of Walters’s complete oeuvre from the late 1930s until his last painting in 1995. A wonderful show, curated by Lucy Hammonds, Laurence Simmons, and Julia Waite, it clearly establishes Walters’s greatness as a painter. Walters’s art was informed and sustained by an extensive knowledge and sophisticated understanding of Euro-American—Piet Mondrian (principally), Sophie Tauber-Arp, Joseph Albers, Auguste Herbin and John McLaughlin, for instance—and Oceanic art, in particular the koru motif of Maori kowhaiwhai (painting, on rafters and paddles, for example) and moko (tattoo). Add to those his early, unusual-in-New Zealand interest in Surrealism and the idiosyncratic sketches of a mentally ill man, Rolf Hattaway. Walters learned about these from a close friend, émigré Dutch artist Theo Schoon, an ardent advocate of Bauhaus practices and Maori visual arts, especially “primitive” rock art.
The resultant body of work constitutes an imaginative and distinctive interweaving of elements from diverse societies and cultures. Formally and technically rigorous, visually refined, conceptually deep, Walters’s paintings are both still and tense. While pulling in different directions, his best known work, the so-called koru paintings, somehow betoken their place, a cluster of islands in the southwest Pacific. Their imprint extends far beyond the art world, to the New Zealand Film Commission’s logo, for instance. Yet, to present Walters’s art only in terms of these koru paintings would skew the overall picture and leave it incomplete. The exhibition rightly gives as much attention to his many other different paintings.

Sydney Parkinson, painted Maori paddle, 1769, Museum of Anthropology and Archaeology, University of Cambridge, UK.
Since Walters’s breakthrough shows at Auckland’s New Vision Gallery in 1966 and 1968 (his first since an early exhibition in 1949), writings about his art have proliferated. His abstractions attracted the keen attention not only of New Zealand art historians, critics, and philosophers, but also the eminent British critic Robert Melville (Architectural Review, 1968), who regarded Walters’s paintings as the best he encountered in New Zealand, polymathic Ernst Gombrich (The Sense of Order, 1979), as well as Australian art historians Rex Butler and A. D. S. Donaldson, and American Thomas Crow (in the present catalogue). The handsome publication reproduces a rich feast of Walters’s works. Nine writers produced eight essays exploring various aspects of Walters’s art and career. Several essays (notably by Peter Brunt and the Australians) offer new details and connections between Walters and other artists.
The trajectory of his career, his primary inspirational sources, his paintings’s formal qualities and conceptual substance, though, have already been intensively excavated, especially by Michael Dunn in the 1970s and 1980s, and Francis Pound from the mid-1980s until his death in 2017.

Gordon Walters, Untitled, 1989, Collection James Wallace Arts Trust, gift of the Rutherford Trust.
In an exhibition review in Art News New Zealand (Summer, 2017), David Eggleton observed, “Curiously, Pound is an absent if also an insistent presence in the catalogue of the show. Although not included as a contributor, many of the ideas and notions first proposed by him appear in the text, subsumed into the writings of others.” And a festschrift in 1989 to mark his 70th birthday, Gordon Walters: Order and Intuition, edited by James Ross and Laurence Simmons, had ten scholarly essays, including (disclosure) my “Walters and Maori Art: the nature of the relationship?”
Transformation of his inspirational sources characterizes Walters’s art. His first investigations of the Maori koru motif, small studies in ink and gouache, appeared in the mid-1950s. They were close to the source; the motif’s organic quality was semi-retained.
In the mid-1960s Walters geometricized the form. Except for circular shapes terminating the crisply delineated bars, curves were straightened out. The reshaped element provided a means, in league with Mondrian et al, for studies in formal relationships using a “deliberately limited range of forms” (Walters, 1966).
These were not intended to draw on the Maori motif’s symbolic values, though Walters’s use of Maori terms for many titles was an acknowledgement of the inspirational importance of Maori art as he had experienced it.
From the mid-1980s, most forcefully in the 1990s, possibly triggered by critiques leveled at the Museum of Modern Art’s 1984-1985 exhibition, Primitivism: Affinity of the Tribal and the Modern, Walters was accused of exploitative appropriation of Maori art by several critics, both Maori and Pakeha (European New Zealander).

Gordon Walters, Gouache, 1957-8, Hocken Collections Uare Taoka o Hākena.
Others, including Maori and Pakeha artists, also defended Walters. The catalogue touches on this sometimes acrimonious argument, though the exhibition’s wall texts and captions bypass it. Deidre Brown’s catalogue essay, “Pitau, Primitivism and Provocation: Gordon Walters’ Appropriation of Maori Iconography,” steers a near-neutral path between the antagonists, culminating with the claim that they moved onto other concerns: “the appropriation debate faded away from academic art history.” Several reviewers, though, questioned whether the contentious issue was satisfactorily addressed by the show.
Most of Walters’s detractors and advocates assumed a straightforward relationship between his work and Maori art: cause = koru motif and effect = the forms in Walters’s koru paintings. The detractors appeared to subscribe to a Manichean structure of polarities in which modernist borrowings are, ipso facto, “bad.” In this system a single component in the works becomes the only or dominant one. If the same paintings are seen within wider cultural and historical contexts, though, an interplay of multiple elements and global connections, in which no single one is dominant, becomes manifest. A complex of factors also mediates how Walters’s koru paintings have functioned. Depending on the kinds of knowledge and cultural baggage individual viewers bring to the encounter, they are clearly perceived very differently. Indeed, one could well wonder whether viewers with opposing perspectives are talking about the same pictures. The diverse opinions resist resolution; the conflicting perspectives are incommensurable. Just as creationists are unlikely to accept a logical refutation of the existence of “God,” so Walters’s critics are not likely to see his art in any other way than their own.
Gordon Walters, Painting No. 1, 1965, Auckland Art Gallery Toi o Tāmaki, Purchase 1965.
Take another slant. In 1910 the New Zealand Herald reported a “curious discovery” by Mme Boeufvre, wife of New Zealand’s French consul. Seeing the Book of Kells (c. 800 CE) in Dublin, she “was much struck by the similarity of Celtic ornaments to Maori conventional designs…how very closely the Maori patterns resembled those of the ancient artists of Ireland.” Since the nineteenth century parallels were frequently drawn between curvilinearities in Maori artifacts and those in the art and ornament of other societies, including such varied cultures and aesthetics as Egyptian, Greek, South East Asian, Victorian, and Art Nouveau, in addition to Celtic. For instance, renowned Austrian art historian Alois Riegl (‘Neuseelandische Ornamentik’, 1891, and Stilfragen, 1896) matched Maori and Egyptian spiraling forms. He noted that they could not possibly have had the same origin. Like many other forms, that of the swastika, for example, the form of the Maori koru motif is found all over the world. There is no singular point of invention.
Universal and local collide in Walters’s painting. Was Walters indigenizing the modern or modernizing the indigenous—or both, or neither? Can we look through several lenses simultaneously? Compelling art certainly can emerge from socio-cultural dissonance—Walters’s paintings continue to energize the spaces they inhabit. They have a contemporary urgency, informing the work of contemporary artists of both Pakeha and Maori descent, such as Darren George and Chris Heaphy. (The latter worked with Walters in his last years.) For others tension between Maori and Euro-American aesthetics and practices remains. Walters’s painterly synthesis of Maori, Oceanic, European, and American elements and ideas was virtually unique among Pakeha artists in his time. He trod a solitary path. In retrospect, though, his oeuvre constitutes a crucial watershed, in which the possibilities of bicultural coexistence of things Maori and Pakeha were explored, celebrated and contested.
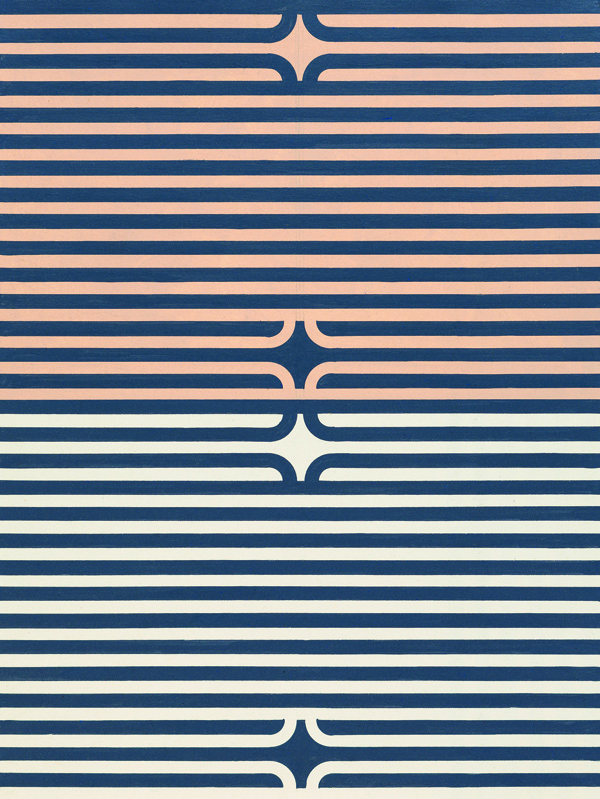

Gordon Walters, Untitled, 1972, Dunedin Public Art Gallery Loan Collection, Courtesy of the Gordon Walters Estate.
Meet the 2019 Travel Grant Recipients
posted by CAA — November 26, 2018
CAA offers Annual Conference Travel Grants to graduate students in art history and studio art and to international artists and scholars. Meet this year’s recipients below.
CAA TRAVEL GRANT IN MEMORY OF ARCHIBALD CASON EDWARDS, SENIOR, AND SARAH STANLEY GORDON EDWARDS
Established by Mary D. Edwards with the help of others, the CAA Travel Grant in Memory of Archibald Cason Edwards, Senior, and Sarah Stanley Gordon Edwards supports women who are emerging scholars at either an advanced stage of pursuing a doctoral degree or who have received their PhD within the two years prior to the submission of the application.

Hollyamber Kennedy, Columbia University
Session: Migration and Colonial Modernities
Paper: Infrastructures of “Legitimate Violence”: Notes on The Prussian Settlement Commission’s Border Villages

Kaja Tally-Schumacher, Cornell University
Session: Perimeter, Periphery, Partition: Exploring Boundaries in Gardens and Landscapes
Paper: A Spectrum of Life: Exploring Blurred Boundaries in Human and Plant Bodies in Roman Gardens
CAA GRADUATE STUDENT CONFERENCE TRAVEL GRANTS
CAA awards Graduate Student Conference Travel Grants to advanced PhD and MFA graduate students as partial reimbursement of travel expenses to the Annual Conference.

J’han Brady
American University

Gabriela Germana
Florida State University

Anthony Hamilton
Illinois State University

Donato Loia
University of Texas at Austin

Marval Rechsteiner
Queer Art Network

Anna Van Voorhis
University of Minnesota-Twin Cities
CAA INTERNATIONAL MEMBER CONFERENCE TRAVEL GRANTS
CAA awards the International Member Conference Travel Grant to artists and scholars from outside the United States as partial reimbursement of travel expenses to the Annual Conference.

Élodie Dupey
Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico

Ana Mannarino
Federal University of Rio De Janeiro, Brazil

Chalice Mitchell
Independent Artist, United Kingdom
SAMUEL H. KRESS FOUNDATION CAA CONFERENCE TRAVEL FELLOWSHIP FOR INTERNATIONAL SCHOLARS
Recognizing the value of first-hand exchanges of ideas and experience among art historians, the Kress Foundation is offering support for international scholars participating as speakers at the 2018 CAA Annual Conference. The scholarly focus of the papers must be European art before 1830. Kress recipients will be announced in January 2019.
CAA-GETTY INTERNATIONAL PROGRAM
Every year since 2012, the CAA-Getty International Program has brought between fifteen and twenty art historians, museum curators, and artists who teach art history to attend CAA’s Annual Conference. This program is funded on an annual basis by the Getty Foundation. Click here to meet the CAA-Getty International Program participants.
CAA Announces 2019 CAA-Getty International Program Participants
posted by CAA — November 02, 2018

CAA is pleased to announce this year’s participants in the CAA-Getty International Program. Now in its eighth year, this international program supported by the Getty Foundation will bring fifteen new participants and five alumni to the 2019 Annual Conference in New York City. The participants—professors of art history, curators, and artists who teach art history—hail from countries throughout the world, expanding CAA’s growing international membership and contributing to an increasingly diverse community of scholars and ideas. Selected by a jury of CAA members from a highly competitive group of applicants, participants will receive funding for travel expenses, hotel accommodations, conference registration, CAA membership, and per diems for out-of-pocket expenditures.
At a one-day preconference colloquium, to be held this year at Parsons School of Design, the fifteen new participants will discuss key issues in the international study of art history together with five CAA-Getty alumni and several CAA members from the United States, who also will serve as hosts throughout the conference. The preconference program will delve deeper into subjects discussed during last year’s program, including such topics as postcolonial and Eurocentric legacies, interdisciplinary and transnational methodologies, and the intersection of politics and art history.
This is the second year that the program includes five alumni, who provide an intellectual link between previous convenings of the international program and this year’s events. They also serve as liaisons between CAA and the growing community of CAA-Getty alumni. In addition to serving as moderators for the preconference colloquium, the five alumni will present a new Global Conversation during the 2019 conference titled Creative Pedagogy: Mapping In-between Spaces Across Cultures.
The goal of the CAA-Getty International Program is to increase international participation in the organization’s activities, thereby expanding international networks and the exchange of ideas both during and after the conference. CAA currently includes members from over 50 countries around the world. We look forward to welcoming the following participants at the next Annual Conference in New York City.
2019 PARTICIPANTS IN THE CAA-GETTY INTERNATIONAL PROGRAM

Richard Bullen is associate professor of art history at the University of Canterbury, New Zealand. He graduated with a PhD from the University of Otago in 2003. Bullen’s principal areas of research are Japanese aesthetics and East Asian art collections in New Zealand. During his years living in Japan, he studied tea ceremony and calligraphy and has since published on aspects of tea ceremony aesthetics. With James Beattie he recently completed a major publicly-funded project to document New Zealand’s largest collection of Chinese art, the Rewi Alley Collection at Canterbury Museum. Their website catalogues all 1400 objects in the collection: http://www.rewialleyart.nz. Together, they also have produced a number of publications, including New China Eyewitness: Roger Duff, Rewi Alley and the Art of Museum Diplomacy (2017) and co-curated three exhibitions. Bullen is currently working on art made in World War II by Japanese POWs held in Australasia.

Pedith Chan is an assistant professor of Cultural Management in the Faculty of Arts at the Chinese University of Hong Kong. She received her PhD in Art and Archaeology from SOAS, University of London. Before joining the Chinese University of Hong Kong Chan was an assistant curator at the Hong Kong Museum of Art, and an assistant professor at the City University of Hong Kong. Her research interests focus on the production and consumption of art and cultural heritage in modern and contemporary China. Recent publications include The Making of a Modern Art World: Institutionalization and Legitimization of Guohua in Republican Shanghai (Leiden: Brill, 2017), “Representation of Chinese Civilization: Exhibiting Chinese Art in Republican China,” in The Future of Museum and Gallery Design (London: Routledge, 2018), and “In Search of the Southeast: Tourism, Nationalism, Scenic Landscape in Republican China,” (Twentieth-Century China, 2018). She is currently researching the making of scenic sites in modern China.

Swati Chemburkar is an architectural historian who lectures and directs a diploma course on Southeast Asian Art and Architecture at Jnanapravaha, a center for the arts in Mumbai, India. In addition, she is a visiting lecturer at the School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS), London, and SOAS’s summer schools in Southeast Asian countries. Chemburkar’s work focuses on eighth- through twelfth-century Southeast Asia, particularly the relationship between texts, rituals, art, architecture, and cross-cultural exchanges in maritime Asia. Her ongoing research explores the spread of the ancient Śaiva sect of Pāśupatas in this region. She has edited Art of Cambodia: Interactions with India (Marg Magazine, Volume 67 Number 2, December 2015-March 2016) and contributed papers to several journals and publications, including the recent “Visualising the Buddhist Mandala: Kesariya, Borobudur and Tabo” in India and Southeast Asia: Cultural Discourse (K. R. Cama Oriental Institute, Mumbai, 2017) and “Pāśupata Sect in Ancient Cambodia and Champa” (co-authored with Shivani Kapoor) in Vibrancy in Stone: Masterpieces of the Đà Nẵng Museum of Cham Sculpture (River Books, 2017).

Stephen Fọlárànmí is a senior lecturer in the Department of Fine & Applied Arts, Ọbáfémi Awólọ́wọ̀ University, Ilé-Ifè, Nigeria. His research focuses on Yoruba art and African mural art and architecture. In particular, Fọlárànmí’s extensive research on the art and architecture of the Òyó and Iléṣà palaces has been published in journals, conference proceedings, and as book chapters. A recent example, “Palace Courtyards in Iléṣà: A Melting Point ofTraditional Yorùbá Architecture,” co-authored with Adémúlẹ̀yá, B.A., was published in Yoruba Studies Review 2, no. 2 (Spring 2018): 51-76. Fọlárànmí was a recipient of the first Höffmann-Dozentur für Interkulturelle Kompetenz at University of Vechta, Germany (2008-09). As an artist Fọlárànmí has exhibited his work in Nigeria, London, Germany, and the United States. He was the chair of the Department of Fine and Applied Arts, Obafemi Awólọ́wọ̀ University, Ile-Ife, between August 2016 and January 2018. Currently, he is a research fellow in the Fine Arts Department, Rhodes University, Grahamstown, South Africa.

Negar Habibi is a Persian art historian and lecturer in Islamic art history at the University of Geneva, Switzerland, where she teaches history of Persian painting from early Islamic times until the modern era. She completed a PhD in 2014 in art history at the Aix-Marseille University in France with a dissertation titled “The Farangi sāzi and Paintings of Ali Qoli Jebādār: an Artistic Syncretism under Shah Soleymān (1666-1694).” Habibi conducts research on paintings from early modern Iran. Adopting a multidisciplinary approach, her work focuses on the career and life of the artist, especially issues of signature authenticity, gender, and artistic patronage in early modern Iranian society. She has published several articles on the art and artists of late-seventeenth-century Iran, and her book titled Ali Qoli Jebādār et l’occidentalisme safavide: une étude sur les peintures dites farangi sāzi, leurs milieux et commanditaires sous Shah Soleimān (1666-94) was published in January 2018 by Brill.

Iro Katsaridou has been the curator of modern and contemporary art at the Museum of Byzantine Culture in Thessaloniki, Greece since 2005. She studied art history at the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki and the Université Paris I-Sorbonne, and also pursued museum studies at the City University of New York. Her doctoral dissertation (Aristotle University, 2010) focused on contemporary Greek photography from 1970-2000. For the past five years Katsaridou has been researching historical photography in Greece, seeking to unravel the role of politics in the formation of photographic representations. In this particular field she also has curated exhibitions of photography and art in wartime (World War I and II) and edited related catalogues. She has co-edited a book about photography during the Nazi Occupation of Greece (1941-1944) and written articles and book chapters on photography (both historical and contemporary), exhibition display policies, as well as the relationship between contemporary Greek art and politics.

Halyna Kohut is an associate professor in the Faculty of Culture and Arts at the Ivan Franko National University of Lviv, Ukraine, where she teaches history of art, contemporary art, and history of theatrical costume. Originally educated as a textile artist, she received a PhD from the Lviv National Academy of Arts with a dissertation on seventeenth- and eighteenth-century Ukrainian kilims. She is the recipient of scholarships and grants from the Austrian Agency for International Mobility and Cooperation in Education, Science and Research, the Canadian Institute of Ukrainian Studies at the University of Alberta, and the Queen Jadwiga Foundation at the Jagiellonian University in Cracow. Kohut studies Ukrainian kilims as an intermediate zone between Oriental and Western design traditions formed on the so-called Great cultural frontier between the Christian West and Islamic East. She is especially interested in the migration of ornamental patterns as well as the articulation of textile’s social and political meanings in the historical context.

Zamansele Nsele is an art historian and a lecturer in design studies in the Faculty of Art, Design and Architecture at the University of Johannesburg, South Africa. She recently submitted her doctoral thesis in Art History & Visual Culture, titled Post-Apartheid Nostalgia and the Future of the Black Visual Archive. In 2018, Nsele was included in the Mail & Guardian’s prestigious list of Top 200 Young South Africans. She has presented her PhD research at Vanderbilt University and Rutgers University (USA), the University of East Anglia (UK), the University of Ghana in Accra (Ghana), and Rhodes University and the University of Cape Town (South Africa). In July 2018, she was a guest speaker at the Museum Conversations Conference hosted by the University of Namibia and the Goethe-Institut Namibia. Her research interests include post-Apartheid nostalgias, contemporary African art, blackface minstrelsy in South African visual culture and Africana studies.

Chukwuemeka Nwigwe is a Nigerian artist and art historian who teaches fashion/textile design and art history at the University of Nigeria Nsukka. He holds a PhD in art history, MFA in textile design, and BA in fine and applied arts from the same university. Nwigwe’s current research is on identity, exemplified in two recent publications: “Fashioning Terror: The Boko Haram Dress Code and the Politics of Identity” (Journal of Fashion Theory, January 2018) and “Breaking the Code: Interrogating Female Cross Dressing in Southeastern Nigeria” (posted online as part of a 2018 ACLS African Humanities Program Postdoctoral Fellowship). Nwigwe also practices as a studio artist. His recent studio experiments with waste plastic, synthetic bags, and foil wrappers, usually woven arbitrarily, have been influenced largely by his research on bird nests begun during his MFA studies.

Oana Maria Nicuță Nae is an assistant professor in the Department of Art History and Theory, Faculty of Visual Arts and Design, George Enescu National University of Arts, Iasi, Romania. She received a PhD in art history from the same university, where she currently teaches courses on the history of modern European art, the history of design, and art and society in modern Europe. Most recently she published “The Materialization of Light in the Art of the (Neo-) Avant-Gardes,” in Objects and Their Traces: Historical Gazes, Anthropological Narratives, Cristina Bogdan, Silvia Marin Barutcieff (coord.), Bucharest University Press (Bucharest, 2018). Nicuță Nae’s current research focuses on the representation of women in Romanian modern art. She also studies multiple modernities, taking into account the particular position of Romanian art narratives in regional and global attempts to construct encompassing ones. Recently she has started parallel research on the notion of influence in nineteenth-century Romanian and European art.

Tamara Quírico is an associate professor in the Art Institute of the Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (State University of Rio de Janeiro, UERJ, Brazil), where she teaches courses to undergraduate students majoring in art history and visual arts and art history courses to graduate students pursuing MA and PhD degrees. She earned her PhD in social history from the Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, in a joint supervision program with the Università di Pisa (Italy), in which she studied changes in the iconography of the Last Judgment in fourteenth-century Tuscan painting. Her dissertation, “Inferno and Paradiso: Representations of the Last Judgment in Fourteenth-Century Tuscan Painting,” was published in Portuguese in 2014. Quírico studies Italian paintings from the thirteenth and fifteenth centuries, focusing in particular on the uses and functions of Christian images, as well as devotional practices and exchanges between Christian images from Europe and Spanish America.

Juliana Ribeiro da Silva Bevilacqua is a specialist in African and Afro-Brazilian art. She studied at the University of São Paulo, where her PhD dissertation was on the Museu do Dundo in Angola (1936–61). From 2004–14 she worked as a researcher at the Museu Afro Brasil in São Paulo. She collaborates with different museums in Brazil researching African art and Afro-Brazilian art collections, including the Museu de Arte de São Paulo and the Museu de Arqueologia e Etnologia at the University of São Paulo. In 2015 she was a guest editor of Critical Interventions: Journal of African Art History and Visual Culture in an issue dedicated to Afro-Brazilian Art. Since 2017 she has been a professor collaborating with the graduate program in Art History at the University of Campinas (Unicamp). Recently she was a visiting professor at the Universidad de Los Andes, Bogota, Colombia, in the Connecting Art Histories program sponsored by the Getty Foundation.

Marko Stamenkovic, born in the former Yugoslavia, is an associate curator of ZETA Contemporary Art Center in Tirana, Albania. He is an art historian and transcultural theorist with a strong interest in the decolonial politics of race, ethnicity, and sexuality. Over the past decade, he has been working primarily in the field of contemporary visual arts as a freelance curator, critic, and writer focused on the intersection of visual thinking and social theories, political philosophies, and cultural practices of the marginalized and the oppressed. He holds a PhD in philosophy from Ghent University (Belgium) where he worked on questions of sacrifice, self-sacrifice in protest, and suicide to explore the relationship between human mortality and politico-economic powers on the darker side of democracy, from a perspective of the global South. He is a member of AICA (International Association of Art Critics) and IKT (International Association of Curators of Contemporary Art).

Viviana Usubiaga holds a PhD in art history from the Universidad de Buenos Aires (UBA) in Argentina. She is an associate professor of contemporary art at the Universidad Nacional de San Martín and an assistant professor of modern and contemporary art history at UBA. Usubiaga is also an adjunct researcher of the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET) and a board member of the Centro Argentino de Investigadores de Arte (CAIA). Her fields of interest include visual arts, literature, and museum studies, focusing on the political impact of transnational circulation of artistic images and texts during socially traumatic periods, including dictatorships and post-dictatorships in South America. Being a specialist in resistance art practices and institutional cultural politics, Usubiaga is the author of Imágenes inestables. Artes visuales, dictadura y democracia en Buenos Aires (2012). She also organizes independent curatorial projects in which she experiments with using scholarly methodologies in non-academic or non-specialist settings.

Jian Zhang was born in Hangzhou, China, and earned his PhD in art theory and history from the China Academy of Art, Hangzhou. He is a professor of art history at the School of Art and Humanities as well as the chief librarian of the Academy Library at the same university. His present research focuses on expressionism (formalism) in modern art historiography as well as the problem of its modernity. He is the author of Life of the Visual Form of Art, The History of the Western Modern Art, and An Alternative Story: Expressionism in the Western Modern Art Historiography, and also the translator of the Chinese edition of Wilhelm Worringer’s Form in Gothic, Heinrich Wolfflin’s The Sense of Form in Art: A Comparative Psychological Study (Italien und das deutsche Formgefühl) and Conrad Fiedler’s On Judging Works of Visual Art.
PARTICIPATING ALUMNI

Sarena Abdullah is a senior lecturer in the School of the Arts at the Universiti Sains Malaysia in Penang, where she teaches art history to undergraduate and graduate students. She received an MA in art history from the University at Buffalo, State University of New York, and a PhD in art history from the University of Sydney in Australia. Specializing in contemporary Malaysian art with a broader interest in Southeast Asian art, Abdullah was the inaugural recipient of the London, Asia Research award given by Paul Mellon Center (London) and Asia Art Archive (Hong Kong). Her book Malaysian Art since the 1990s: Postmodern Situation was published in 2018, as was Ambitious Alignments: New Histories of Southeast Asian Art, for which she was a co-editor, published by the Power Institute and National Gallery Singapore. She first participated in the CAA-Getty International Program in 2016 and presented a paper as part of the program’s reunion during the 2017 conference.

Katarzyna Cytlak is a Polish art historian based in Buenos Aires, Argentina, whose research focuses on Central European and Latin American artistic creations in the second half of the twentieth century. She studies conceptual art, radical and utopian architecture, socially engaged art, and art theory in relation to post-socialist countries from a transmodern and transnational perspective. In 2012, she received a PhD from the University Paris 1 Panthéon-Sorbonne, France. Cytlak was a postdoctoral fellow at the CONICET – National Scientific and Technical Research Council, Argentina (2015-2017). She is currently working as a researcher and professor at the Center for Slavic and Chinese Studies, University of San Martín, Argentina. Selected publications include articles in Umění/Art, Eadem Utraque Europa, Third Text, and the RIHA Journal. Cytlak is a grantee of the University Paris 4 Sorbonne (Paris), the Terra Foundation for American Art (Chicago, Paris) and the Institut National d’Histoire de l’Art (INHA, Paris). In 2018, she participated in the CAA-Getty International Program.

Nadhra Khan is a specialist in the history of art and architecture of the Punjab from the sixteenth to the early twentieth century. She received a PhD from the University College of Art & Design, University of the Punjab, Lahore, and teaches art history at Lahore University of Management Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan. Khan’s research focuses on the visual and material culture of the Punjab region during the Mughal, Sikh, and colonial periods. Her publications address several misconceptions and misrepresentations of Mughal and Sikh art and architecture as well as the state of art and craft in the Punjab under the British Raj and reflect the wide range of her interests and expertise.

Nazar Kozak is a senior research scholar in the Department of Art Studies in the Ethnology Institute at the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine. Previously he also taught the history of art at the Ivan Franko National University of Lviv. Kozak has received scholarships and grants from the Fulbright Scholar Program, State Scholarships Foundation of Greece, the American Council of Learned Societies, the Austrian Agency for International Mobility, and the Shevchenko Scientific Society in the United States. Kozak’s primary research is on Byzantine and post-Byzantine art in Eastern Europe. He is the author of Obraz i vlada: Kniazhi portrety u mystetstvi Kyïvskoï Rusi XI stolittia (Image and authority: Royal portraits in the art of Kyivan Rus’ of the eleventh century, Lviv, 2007). More recently, he has begun to work on contemporary activist art. His article on the art interventions during the Ukrainian Maidan revolution was published in the Spring 2017 issue of the Art Journal; it received an honorable mention as a finalist for that year’s Art Journal Award. Kozak participated in the CAA-Getty International Program in 2015 and presented a paper as part of the program’s reunion during the 2017 conference.

Chen Liu teaches art history and architecture at Tsinghua University in Beijing, China, where she received a bachelor’s degree in architecture with honors. After receiving a master’s in architecture and urban planning from the University of Maryland in 2000, she practiced as an architect in Washington DC until 2005. In 2011, she received a PhD in art history from Princeton University, specializing in Renaissance and Baroque art and architecture. In 2012, funded by an Andrew W. Mellow Fellowship, she helped create and direct the first Villa I Tatti summer research seminar designed specifically for Chinese scholars. “The Unity of the Arts in Renaissance Italy” provided participants with the opportunity to study firsthand the art and architecture of Renaissance Italy. Liu also teaches courses on the visual arts at Beijing Film Academy and Tongji University (Shanghai). She publishes widely on early modern art and architecture, as well as on the response of Chinese scholars to the Italian Renaissance. For the academic year 2018-2019 Liu is a Harvard-Yenching Institute Visiting Scholar at Harvard University.
International Review: L’Algérie de Gustave Guillaumet by Roger Benjamin
posted by CAA — October 26, 2018
The following article was written in response to a call for submissions by CAA’s International Committee. It is by Roger Benjamin, professor of art history, University of Sydney, Australia.
Exhibition review: L’Algérie de Gustave Guillaumet (1840-1887), Musée des Beaux-Arts de La Rochelle (France), June 8-September 17, 2018
In a most unassuming regional museum in France, an exhibition of real art-historical significance opened this past June. For the first time since 1899, the work of the preeminent French Orientalist painter of the later 19th century has been brought together. Gustave Guillaumet is not an obscure artist, as every survey of Orientalism since the great Royal Academy show of 1984 has included his paintings. But the scholarly work had not been done until now, when the fruits of Marie Gautheron’s 2015 doctoral dissertation on the desert and Guillaumet have been brought to bear (Gautheron, M., L’invention du désert: émergence d’un paysage, du début du XIXe siècle au premier atelier algérien de Gustave Guillaumet (1863-1869), Paris Nanterre University).

Fig. 1. Gustave Guillaumet, La Famine en Algérie, Salon of 1869, oil on canvas, 122 x 92 in (309 x 234 cm) Le Musée National Public Cirta de Constantine, Algeria (restored for the exhibition).
Many of the works on view in La Rochelle are unfamiliar, coming from regional museums, the artist’s descendants, private enthusiasts, and storage collections of the Musée d’Orsay. The largest single work was thought to have been lost. The Famine in Algeria (Fig. 1), the most disturbing large scale canvas at the Salon of 1869, was known only by a poor woodcut and several drawings. Its subject was altogether too tough—the cadaverous members of two Arab families expiring on the pavement of a city in what was (in French law) a department of France, the province of Algiers in Algeria.
La Famine had been languishing, rolled up and torn in the basement of the National Public Museum of Constantine, Algeria (Le Musée National Public Cirta de Constantine). The research of Dr. Gautheron located it, and through the goodwill of Algerian curators and the political weight of Maître Salim Becha (an Algiers-based lawyer, art collector and philanthropist) the work was sent to France for restoration. A successful crowd-funding campaign led by Annick Notter, chief curator at La Rochelle, paid for the conservator Pascale Brenelli, who spent nine hours every day from early February until mid-June resurrecting the picture.
Guillaumet’s ghastly image of a baby suckling at the collapsed breast of its dead mother goes back through Eugène Delacroix to Nicolas Poussin and classical precedents. Entirely new, however, is his angular figure of an emaciated Arab father who, supporting his fainting teenage son, reaches up for a loaf of bread being handed down from the tiny window of a prosperous home. The outstretched hand is female, bejeweled and, through the curvature of its fingers, evocative of the Jewish beauties painted by Chasseriau in Constantine (1846) and by Delacroix in Tangier (1832).
La Famine’s grisly treatment was probably influenced by photographs of the dying taken in situ. Catalogue author (and leading historian) Jacques Frémaux estimates one third of the indigenous population of Algeria died in the famine of 1866-70, due to drought, locust plague, cholera, and the expropriation of farmlands by European settlers. La famine is unrelieved by aesthetic ‘sweet spots’ like the majestic horseman that Delacroix placed in his Massacres of Chios. We have instead the moral and visual austerity that pervades Guillaumet’s work. A grave witness to these events, Guillaumet was not about to beautify them.

Fig. 2. Gustave Guillaumet, La Séguia, près de Biskra, oil on canvas, 1884, Salon of 1885, 39 x 61 in (100 x 155.5 cm), Musée d’Orsay, Paris.
Almost all of the artist’s best-known landscapes are on view, including The Sahara of 1867, with its camel skeleton and mirage at the horizon with a setting sun, and the dazzling Séguia, Biskra (Fig. 2) of 1884. (Both are usually on display at the Musée d’Orsay). The loan of numerous restored pencil drawings and watercolors from the Orsay was intended to show the genetic relationship between such studies and the resultant tableaux by Guillaumet (who narrowly missed the Prix de Rome for landscape and ended up heading to Algiers in 1862 rather than Rome). (Fig. 3)
It came as a shock to learn that many of these drawings could not be exhibited on the second floor of the eighteenth-century mansion that houses the Musée de la Rochelle, as it was condemned by city architects one week before the scheduled opening. Despite the best efforts of the staff, this major exhibition was opened in almost third world conditions: a building with the floor above held up by a dozen massive steel columns, no air conditioning, and inadequate spotlighting. Yet historic La Rochelle is a wealthy city, with a new 5,000-boat marina and an opulent public library, the Mediathèque, nearby. City and provincial authorities must reward the enterprise of its art curators by providing an adequate home for future temporary exhibitions and permanent collections.

Fig. 3. Gustave Guillaumet, Sous la tente, graphite pencil on paper, 9.5 x 17 in (24 x 44 cm), private collection. Photo: A. Leprince.
Fortunately, L’Algérie de Gustave Guillaumet will travel to two other regional museums in much better condition: the Limoges Fine Arts Museum and the celebrated La Piscine, a converted Art Nouveau baths complex in the northern city of Roubaix. And happily, the catalogue, a scholarly book with first-class production values and superb plates, perfectly represents the project. Its backbone is the set of four chapters by Gautheron, a former academic teaching art history and visual culture at the École normale supérieur de Lyon, along with detailed entries on key works and a documentary apparatus at the end. Gautheron was careful to enlist a range of other writers, including Algerian literary figures like Leïla Sebbar, and art historians from Algeria, the United States, Australia, France, and Ireland. For her part Gautheron has also completed a 300-page monograph on Guillaumet that is awaiting publication.
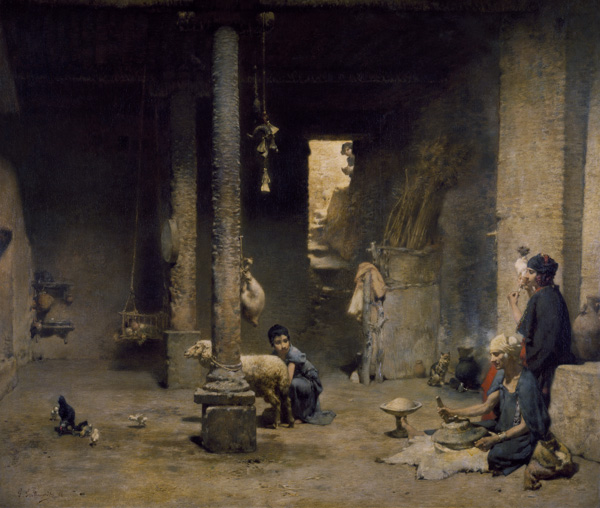

Fig. 4. Gustave Guillaumet, Habitation saharienne (Cercle de Biskra), Salon of 1882, oil on canvas, 58 x 68 in (146.1 x 173.4 cm), Chrysler Museum of Art, Norfolk, Virginia, gift of Walter P. Chrysler, Jr.
Guillaumet, like the admirable Eugène Fromentin before him, traveled initially in Algeria in close connection with the officers of the French army and its political wing, the Bureau Arabe. His stunning series of interiors of Arab houses, made in the oasis villages of Biskra and Bou-Saâda, were made possible by the intervention of the Commandant’s wife (as the artist narrates in his text “Les intérieurs,” from his book Tableaux Algériens). Crowning the series but absent from the exhibition was the key Guillaumet work in America, Saharan Dwelling (Fig. 4), recently loaned by the Chrysler Museum of Norfolk Virginia to the Institut du Monde Arabe in Paris (see the author’s Biskra, Sortilèges d’une oasis, Paris and Algiers, 2016, pp. 90-91). Scenes of women and their daughters working at looms, the first of their kind and highly influential on the next generation, complement Guillaumet’s earlier assemblages of men, camels and horses on the barren plains—at prayer, at market, or on a military bivouac. Guillaumet, an admirer of J. F. Millet, produces high naturalism, except in one key respect: he always excludes the colonizer and his works. Absent are the soldiers in uniform, colonists directing Berber farmworkers, the modern buildings and telegraph wires at Bou-Saâda, the military hospital at Biskra where the painter convalesced in 1862, or the British tourists who by the 1880s were encumbering the desert scene. Guillaumet’s vision is not a “painting of modern life” as exemplified by the traveler Constantin Guys in Istanbul. It is an image of Algeria as it used to be: a country and a people that won the admiration of foreign travelers, intellectuals and officers, even as their invasive actions helped bring about its demise.
Member Spotlight: Pauline Chakmakjian, Visit Kyoto Ambassador
posted by CAA — October 25, 2018
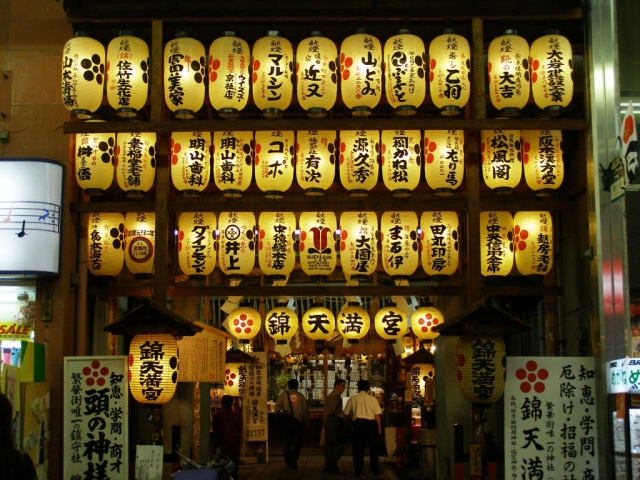

Lanterns lit in Teramachi Street, Kyoto. Photo: Pauline Chakmakjian, MA
Coming up in the spring of next year, we’re pleased to partner with Martin Randall Travel to offer a trip for scholars and artists to Japan. “Understanding Japan for CAA – Arts & Crafts, History, Religion & Traditions” will take place May 9-20, 2019, and will be led by independent Japan scholar and CAA lifetime member, Pauline Chakmakjian.
As a lifetime member and a specialist who lectures on a variety of subjects related to the history, fine arts, and culture of Japan, we wanted to highlight the work Pauline is doing in our Member Spotlight series. Read our interview with her below.

Pauline Chakmakjian, Freeman of the City of London, September 2018. Photo: Pauline Chakmakjian, MA
Joelle Te Paske: Hi Pauline. Thanks for taking the time to answer our questions. So to begin, where are you from originally?
Pauline Chakmakjian: I was born in Los Angeles, California.
JTP: What pathways led you to the work you do now?
PC: My primary passions are travel and the arts. The associations and networks I have developed throughout the years have naturally led to projects that combine this fondness for both cultural variety and the diversity of thought and creativity in various countries, especially Japan.

Temple in Kyoto. Photo: Pauline Chakmakjian, MA
JTP: When did you first become a CAA member?
PC: In the summer of 2015, in order to support art and art education.
JTP: Why are you a life member? What has that meant to you?
PC: I think in a long-term manner and carefully select organizations to support that reflect my own interests. With time, becoming a life member will increase in value for me personally, since CAA is focused on art and art makes life exceptionally rich and pleasant. My preference is to support things that encourage creativity and beauty—arts and culture are what makes us human.
JTP: Have you attended CAA conferences?
PC: I have not yet had the pleasure of attending a CAA conference due to my previous travel commitments, but certainly plan to in the future.
JTP: The upcoming tour—“Understanding Japan for CAA – Arts & Crafts, History, Religion & Traditions”—is specifically designed for CAA members. What are you most excited for?
PC: The Kyoto part of the trip, which is towards the end of the tour, of course! In so many ways, the old capital of Kyoto is the heart of Japan, from artistic and culinary traditions that are over one thousand years old, to the eternal backdrop of the tastes and pastimes of the nobility of the Heian-period court, which have cascaded down to influence generations of Japanese people ever since.
JTP: What is the most surprising thing for people to know about Japanese art history?
PC: There are many surprises for those who have never been to Japan or studied its artistic heritage, but if I had to choose one it would be that much of the traditional look or aesthetics of Japanese art are manifestations of the preferences of the upper tiers of the hierarchical class system the Heian court of one thousand years ago, borrowed from the ancient Imperial Chinese court in Chang’an (Xian). The upper two tiers consisted of the Emperor and his retinue of courtiers first, and then the warrior class. These two classes were largely responsible for the distinctive elements and emphases found in Japanese art, from landscape architecture to painting to teaware.

Doll of Lady Murasaki Shikibu, Kyoto. Photo: Pauline Chakmakjian, MA
JTP: Can you tell our members one unforgettable travel story?
PC: Yes, sailing to Easter Island was probably the most adventurous thing I’ve attempted travel-wise. From Tauranga to Hanga Roa I was on board a two-masted brigantine with a permanent and voyage crew for 33 days of sailing across the Pacific. I had always wanted to visit Easter Island and this travel journey combined this dream with my love of classical sailing ships. We were also given instruction on celestial navigation over the course of the sailing experience.
The image that stays in one’s mind and feeling of sailing through a gale force 8 storm at the helm is thrilling. I love paintings by Montague Dawson and this was like one of his paintings in motion.

Montague Dawson, A Night at Sea, n.d. (Artwork in the public domain, via Flickr)
JTP: What advice would you give someone looking to partner with travel agencies and lead the sort of tours you do?
PC: A broad range of knowledge on the destination is essential. Though the focus is usually on the arts in terms of cultural travel companies, the tour leader will be asked about the other aspects of the country such as its politics, economy, technology, and other areas, so it’s not enough to simply know about fine art, music, and the performing arts.

Heian Shrine, Kyoto. Photo: Pauline Chakmakjian, MA
JTP: What is your top recommendation (such as a book, website, or resource) for people working in the arts right now?
PC: There are so many resources both offline and online depending on one’s particular focus or interest in the arts, but I do quite like the international edition of The Art Newspaper. It’s particularly handy for people who travel a lot.
JTP: Do you have a favorite artist or artwork?
PC: This is difficult to answer as there are so many talented people who have created beauty of various types in this world, but the moment that made me want to lecture on art was during my undergraduate studies after I gave a talk for over an hour on The Garden of Earthly Delights by Hieronymous Bosch. This triptych is truly one of the most unique and extraordinary works of art ever made. The eccentricities within each section of the triptych as well as Bosch’s personal associations is what also partly made me curious about private, esoteric networks such as Freemasonry, which I also lecture on.
Pauline Chakmakjian is an independent lecturer on a variety of subjects related to the history, fine arts and culture of Japan. She lectures for private member societies, corporate entertainment, private homes, universities, cruises, charities and other related organizations including lecture tours in Australia and New Zealand. She holds a BA in English Literature during which she was also awarded a Merit Scholarship in Fine Art, a Diploma in Law, an MA in Modern French Studies and is a member of the Honourable Society of the Inner Temple. Pauline was elected onto the Board of the Japan Society of the United Kingdom from 2008–2014 and the Japan Society of Hawaii from 2015–2017. In 2014, Pauline was appointed a Visit Kyoto Ambassador by the Mayor of the City of Kyoto.
CAA Announces Exclusive Member Trip to Japan
posted by CAA — October 09, 2018

Makino Heinei gets blown away in the storm, an illustration from Ancient Tales & Folklore of Japan by R. Gordon Smith, 1908
Understanding Japan for CAA – Arts & crafts, history, religion & traditions
May 9-20, 2019
CAA is pleased to partner with Martin Randall Travel to offer an exclusive trip for scholars and artists to Japan.
“Understanding Japan for CAA – Arts & Crafts, History, Religion & Traditions” will take place May 9-20, 2019, and will be led by independent Japan scholar and CAA lifetime member, Pauline Chakmakjian.
Designed specifically for CAA members, this extensive tour will take visitors to the heart of Japan to explore its art and architecture, the continuing work of its craftspeople, its natural beauty and heritage, and modern Japan and its position in the world. Beginning in Tokyo, Understanding Japan for CAA promises to be a remarkable opportunity to engage with many aspects of the country. The tour features:
- Modern architecture in Tokyo and the contrasting traditional buildings in Shirakawa and Takayama.
- Stunning Buddhist temples and gardens in Kyoto, and the legendary, ancient shrine at Izumo.
- Traditional arts and crafts in Kanazawa.
- Overnights in a traditional ryokan (Japanese inn) and an onsen hotel (with natural hot spring bathing options).
- An exploration of the Japanese character in history and today, with specialist lectures by Pauline Chakmakjian.
More about Pauline Chakmakjian

Pauline Chakmakjian is an independent lecturer on a variety of subjects related to the history, fine arts and culture of Japan. She lectures for private member societies, corporate entertainment, private homes, universities, cruises, charities and other related organizations including lecture tours in Australia and New Zealand. She holds a BA in English Literature during which she was also awarded a Merit Scholarship in Fine Art, a Diploma in Law, an MA in Modern French Studies and is a member of the Honourable Society of the Inner Temple. Pauline was elected onto the Board of the Japan Society of the United Kingdom from 2008–2014 and the Japan Society of Hawaii from 2015–2017. In 2014, Pauline was appointed a Visit Kyoto Ambassador by the Mayor of the City of Kyoto.
A portion of the proceeds from every trip will support CAA and its mission to advance art and design.
CAA Statement on Supreme Court Decision to Uphold Travel Ban
posted by CAA — June 26, 2018
In light of today’s Supreme Court ruling upholding President Trump’s travel ban, we are reposting our Statement from February 2017 here in its entirety. Our values have not changed.
As we stated when we joined two amicus briefs in May 2017, speaking out against this decision is inherent to our advocacy efforts and our international reach at CAA. The travel ban impacts the international attendees of our Annual Conference, it impinges on the flow of information and discussion between colleagues, and it harms the practice of research more broadly. See the statement below.
CAA Statement on Immigration Ban, February 2017
CAA, the largest professional group for artists and art historians in the United States, strongly condemns and expresses its grave concern about the recent presidential executive order aimed at limiting the movement of members of CAA and the broader community of arts professionals who fall under the selective set of criteria for national status or ethnic affiliation.
CAA has counted international scholars and artists among its members for many years. Committed to the common purpose of understanding the visual arts in all its forms, professionals throughout the world have enriched CAA’s community by adding diverse perspectives to the study, making, and teaching of art. With funding in recent years from the Getty Foundation to support travel and programs for scholars and curators from Africa, Latin America, Russia and Eastern Europe, and Asia, the association now includes members from seventy countries. More than ten percent of our individual members are international. CAA has counted international scholars and artists among its members since the earliest years of its existence. The roots of CAA’s present-day international program stemmed from a desire to assist European refugees in the 1930s to support personal safety as well as academic and artistic freedom. During that decade, CAA had a “foreign membership” category; as art historians fled Hitler’s Europe, CAA ran a lecture bureau for refugee scholars that created speaking engagements for them at institutions throughout the United States.
The recently announced ban on travel to the United States for residents of seven predominantly Muslim countries not only goes against the inclusive, secular underpinnings of American democracy, it stifles the open access to scholarship and art upon which our work is founded. The executive order goes against our professional and scholarly commitment to diversity, the global exchange of ideas, and the respect for difference. The contribution of immigrants, foreign nationals, and people of all cultural backgrounds greatly strengthens our intellectual and creative world. Further, we believe the executive order law challenges the values at the heart of the US Constitution’s protections on speech and association as well as our national commitment to democratic process for all.
Turning our backs on refugees and closing our borders selectively stifles creative and intellectual work in addition to its very real impact on peoples’ daily lives. We call on our public officials to thwart this attempt to seemingly preserve our own safety at the expense of those who are vulnerable and who also contribute so much.
Without question, CAA welcomes all members and non-members to our upcoming Annual Conference to discuss and debate what constitutes a thriving artistic and intellectual society. Such openness is essential to our mission. We are committed through dialogue and action to help any CAA members who are affected by this policy. To this end, the association and the Board of Directors will continue to monitor and respond to policies related to this order as well as pressure for its immediate repeal.
See the original statement posted February 2017.
See CAA Amicus Brief on Trump’s Travel Ban, May 2017.
For more on CAA’s advocacy efforts, click here.
Apply for the 2019 CAA-Getty International Program
posted by CAA — June 11, 2018
Nomusa Makhubu, University of Cape Town, chair of the “Border Crossings: The Migration of Art, People, and Ideas” alumni panel at CAA 2018. Photo: Rafael Cardenas
The CAA-Getty International Program, generously supported by the Getty Foundation, provides funding to between fifteen and twenty art historians, museum curators, and artists who teach art history to attend CAA’s Annual Conferences. The goal of the project is to increase international participation in CAA, to diversify the association’s membership, and to foster collaborations between North American art historians, artists, and curators and their international colleagues.
ABOUT THE 2019 GRANT
The 2019 CAA-Getty International Program will support fifteen art historians, museum curators, and artists who teach art history to attend the 106th Annual Conference, taking place in New York City from February 13-16, 2019. The grant covers travel expenses, hotel accommodations for eight nights, per diems, conference registrations, and one-year CAA memberships. The program will include a one-day preconference colloquium on international issues in art history on February 12, at which grant recipients will present and discuss their common professional interests and issues. Attendance at the preconference is limited and by invitation only. This year the grant also will fund five alumni from the CAA-Getty International Program to participate in the preconference colloquium and speak at a session during the conference. As they have in previous years, representatives from CAA’s membership will host program participants during the conference week.
ARE YOU ELIGIBLE?
Applicants must be practicing art historians who teach at a university or work as a curator in a museum, or artists who teach art history. They must have a good working knowledge of English and be available to participate in CAA events from February 12-16, 2019. Only professionals who have not attended a CAA conference previously, and who are from countries underrepresented in CAA’s membership are eligible to apply. The grant excludes scholars from North America, Western Europe, and Australia, whose countries are well represented in CAA. It further excludes scholars who have received funds from American foundations or research institutes to participate in conferences or residencies in the United States. Applicants do not need to be CAA members. This grant program is not open to graduate students or to those participating in the 2019 conference as chairs, speakers, or discussants.
HOW TO APPLY
Please review the application specifications and complete the application form. PLEASE NOTE: In order to apply, you need an temporary Member Number, which you get by contacting Member Services. If you have questions about the process or are unsure of your eligibility, please email Janet Landay, project director of the CAA-Getty International Program.
Applications should include:
- A completed application form
- A two-page version of the applicant’s CV
- A letter of recommendation from the chair, dean, or director of the applicant’s school, department, or museum
Applications must be submitted no later than Monday, August 27, 2018. Only applications submitted via the online form will be considered. CAA will notify applicants by Friday, October 5, 2018.



